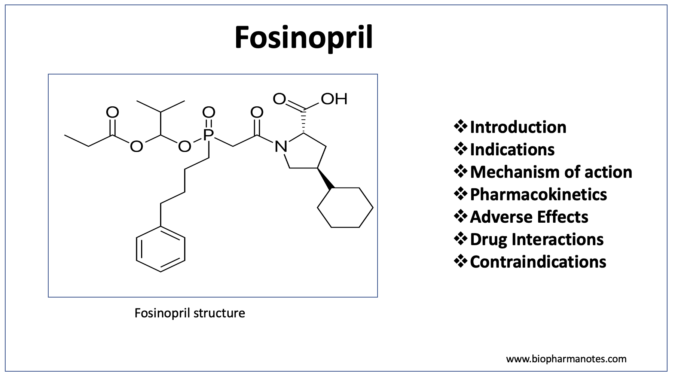
- Fosinopril is a phosphinic acid containing ester prodrug belonging to class of drug called ACE (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme) inhibitor. ACE (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme) inhibitors or ACE-I are among the most widely used cardiovascular medicines. Their introduction in 1980s improve the management of hypertension
- It was approved for medical use by FDA in 1991. It contains phosphinate group which can bind to active site of ACE and inhibit it.
Indications of Fosinopril
- In treatment of mild to moderate hypertension.
- Used to slow the progression of renal disease in hypertensive patient with diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria.
- Used as additional agent in treating heart failure.
- Its off-label uses include treatment of HIV- associated nephropathy.
Mechanism of action of Fosinopril
- Fosinopril is prodrug and is hydrolyzed to its active form, fosinoprilat in liver. Fosinoprilat exerts its action by antagonizing the effect of RAAS system (Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System). RAAS system play important role in regulation of hemodynamics, water, and electrolyte balance.
- It inhibits RAAS by inhibiting the enzyme, ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme). ACE cleaves inactive angiotensin I to active angiotensin II which is a potent vasoconstrictor. ACE is also involved in breakdown of bradykinin, a peptide that increases production of nitric oxide and prostacyclin, both of which are potent vasodilators.
- Fosinoprilat competitively inhibits ACE and inhibits conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. It results in prevention of:
- Pressor effect of angiotensin II.
- Stimulation of aldosterone synthesis and release resulting in decreased sodium and water retention.
- Metabolism of bradykinin by ACE.
- Thus, vasodilation of both arterioles and veins occurs because of decreased vasoconstriction (due to decreased angiotensin II) and enhanced vasodilation (due to increased bradykinin). The overall result is decrease of blood pressure.
Pharmacokinetics of Fosinopril
- It is administered via oral route and had slow and incomplete absorption after oral administration. Food may decrease its rate of absorption but not extent of absorption. Peak plasma concentration of fosinoprilat is achieved within 3 hours of administration.
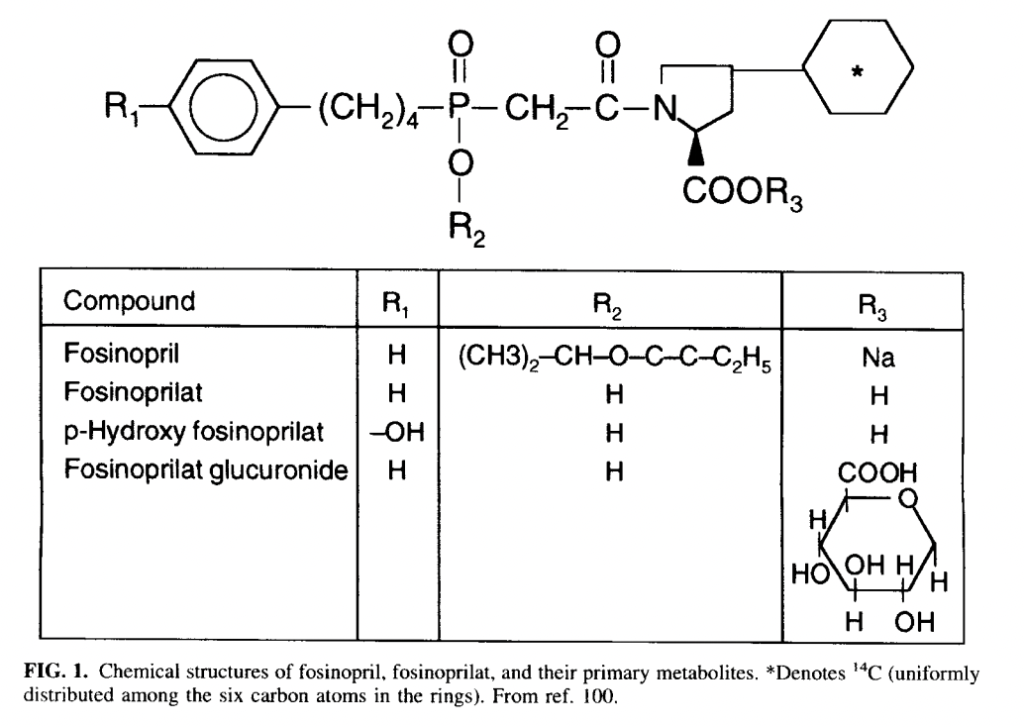
- Ester moiety of fosinopril is cleaved by hepatic esterase in liver to convert it into fosinoprilat. 75% of fosinopril is metabolized to fosinoprilat and remaining amount is metabolized to other metabolites including glucuronide conjugate of fosinoprilat.
- 50% of drug is excreted via urine and 50% via feces. Its half-life is around 12 hours. Dosage reduction is required in renal patients or in patients with water or sodium (Na+) depletion.
Adverse effects
- Its long-term use can cause dry cough due to accumulation of bradykinin. It is often mild but may be troublesome and occurs in around 5-30% of cases.
- Angioedema may occur rarely but is severe, life-threatening side effect associated with fosinopril.
- Other side effects include GI disturbances, fatigue, dizziness, elevation in serum aminotransferase concentration and acute liver damage.
Drug Interactions
- Co-administration with aliskiren may increase severity of side effects of fosinopril including hyperkalemia, hypotension, and nephrotoxic effect. Hence, this combination should be avoided. Concurrent administration with potassium sparing diuretics may increase risk of hyperkalemia.
- Fosinopril may inhibit metabolism of lithium and increase its concentration leading to increase in side effects of lithium. Drugs like antacid may reduce serum level of fosinopril by altering its absorption.
- Co-administration of fosinopril with NSAIDs like aspirin, paracetamol may cause impairment of renal function leading to acute renal damage.
Contraindications
- Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to fosinopril or any other ACE inhibitors.
- Fosinopril can cross placenta and cause fetal malformation or death of fetus. Hence, it is contraindicated in pregnancy or if someone is planning for pregnancy like other ACE inhibitors.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554480/
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00492
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2003/19915se5-037_monopril_lbl.pdf
- Sica DA et al. Fosinopril: Emerging Considerations and Implications for Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Therapy. Cardiovascular Drug Reviews. 1998; 16(4): 319-345.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- Pharmacology and pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.