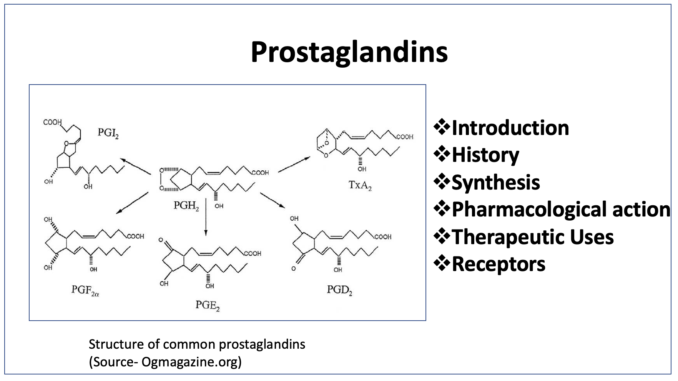
- Prostaglandins are endogenously produced compounds which have different effect on human physiology.
History
- Kuzrok and Lieb demonstrated activity of human semen on isolated strips of human uterine muscle in 1930. And in 1935, von Euler discovered that substance present in human semen is responsible for causing contraction of isolated intestinal and uterine muscle. He named these substance ‘prostaglandins’ due to their probable origin from prostate.
- In 1982, Bergstorm and team discovered that prostaglandins are related derivatives of lipid soluble prostanoic acid.
Synthesis of prostaglandins
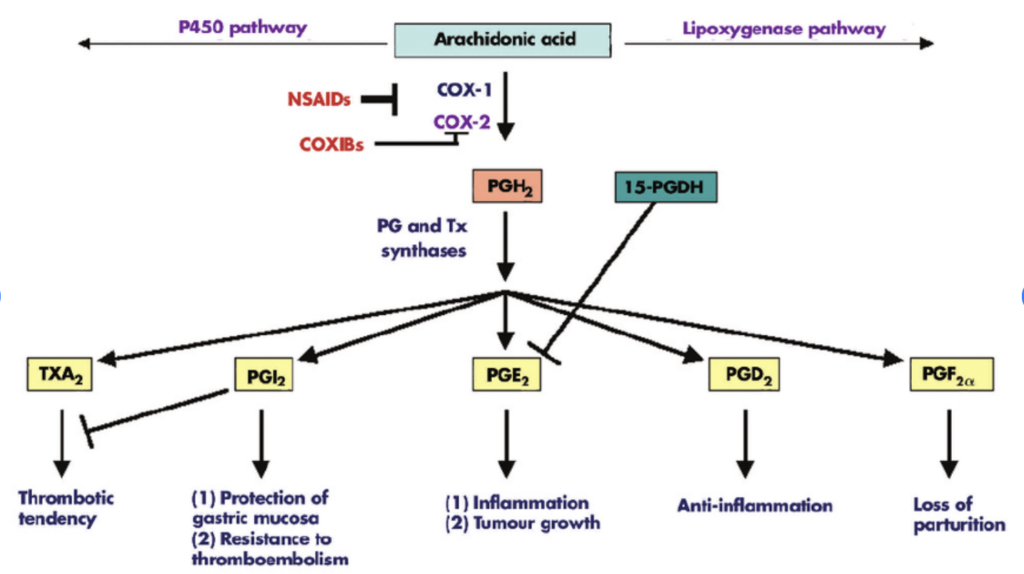
Figure- Overview of synthesis and functions of prostaglandins (Source- Wang D et al, 2006)
- Prostaglandins consist of unsaturated fatty acid with cyclopentane ring. Arachidonic acid, which is constituent of phospholipid of cell membrane, is major precursor of prostaglandins.
- Various stimuli like physical agents and chemicals, hormones may activate enzyme called phospholipase A2 which catalyze release of arachidonic acid from phospholipid. The released arachidonic acid than undergoes two separate pathways, cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway. Prostaglandins are produced by COX pathway. LOX pathway is responsible for production of leukotrienes.
- Two cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 play important role in conversion of arachidonic acid to one of several possible endoperoxide which undergo further modification to form prostaglandins, thromboxane, and prostacyclin.
- COX-1 is constitutive and responsible for physiologic production of prostanoids, and COX-2 is inducible and causes elevated production of prostanoids.
Pharmacological actions of prostaglandins
- Prostaglandins are found in almost every tissue in human body and have different effects on different system. Their different action is due to difference in their structure and the type of receptor to which they bind.
In Gastrointestinal system
- PGE2 and PGI2 have cytoprotective effect on gastric and duodenal mucosa. They inhibit secretion of gastric acid and enhance mucosal blood flow. This is the reason NSAIDs like aspirin which inhibit prostaglandin synthesis may cause peptic ulcer.
Cardiovascular system
- PGE2 and PGI2 are potent vasodilators and cause dilation of arterioles and postcapillary venules.
Reproductive system
- They stimulate uterine smooth muscle.
Kidney
- PGE2 and PGI2 exert direct action on renal tubules and cause diuresis, natriuresis and kaliuresis.
Smooth muscle
- PGE2 and PGF2a stimulate smooth muscle of myometrium and also increase intestinal motility.
Platelet aggregation
- PG endoperoxide and TXA2 causes platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction. Platelet aggregation begins the formation of blood clot. However, PGI2 inhibits platelet aggregation and cause vasodilation.
Inflammation and immunity
- Prostaglandin play major role in inflammation. They inhibit immune response by inhibiting lymphocyte formation and proliferation.
- PGE2 decreases humoral antibody response. PGD2 acts as chemoattractant for eosinophils and induce chemotaxis and migration of Th2 lymphocytes.
Eye
- PGF2a increases aqueous humor outflow of eye vi uveoscleral and trabecular meshwork pathway and decrease intraocular pressure.
Therapeutic uses of prostaglandins
As prostaglandins play major role in many physiological functions, modulation of pain, fever, and inflammation, they are used in various therapeutic purpose. Some of such uses are:
Alprostadil– PGE1 analogue used to treat erectile dysfunction and to maintain patency of ductus arteriosus.
Lubiprostone– PGE1 derivative used to treat irritable bowel syndrome with constipation, opioid induced constipation, and chronic idiopathic constipation.
Misoprostol– PGE1 analogue which is used as gastric cytoprotective. It is available in combination with NSAIDs like diclofenac to protect mucosal lining of stomach due to chronic use of NSAIDs.
PGI2 analogues- Epoprostenol and treprostinil are used in treating pulmonary arterial hypertension. Epoprostenol is also used in peripheral vascular disease.
PGF2a analogues– Latanoprost, tafluprost and bimatoprost are used in treatment of open angle glaucoma.
Prostaglandin receptors
- Most of the PGs have local action- act locally near site of formation. All of the prostaglandin receptors are GPCR (G protein coupled receptor). There are 9 known prostaglandin receptors.
- PGs bind to these receptors and activate secondary signaling pathway by modulating activities of phospholipase C and adenylyl cyclase.
References
- https://www.britannica.com/biography/John-Vane
- https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/27830
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7643103_Prostaglandins_And_Cancer
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.