- Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic disorder which occurs due to mutation occurring in a gene in X chromosome. Fragile X syndrome is inherited from parents to children and is the cause of developmental and intellectual disabilities. It is most common inherited disease causing intellectual and developmental disabilities.
- Synonym- Martin Bell Syndrome. Martin and Bell first described about FXS as a type of intellectual disability in 1943.
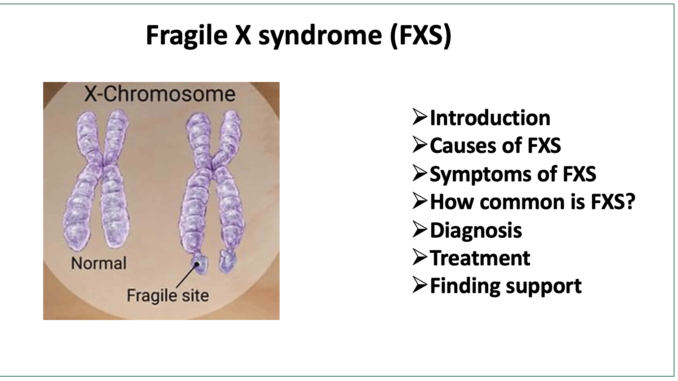
- The name Fragile X syndrome is due to fragile or broken looking X chromosome under microscope. There are two more syndrome belonging to fragile X family disorder. They are Fragile X- associated tremor/ ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) and Fragile X- associated primary ovarian insufficiency (FXPOI).
Cause of Fragile X Syndrome
- It occurs due to mutation in FMR1 (fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1) gene located on X chromosome. This gene plays major role in making of protein called FMRP (fragile X mental retardation 1 protein) which is important for brain development, and regulation of synaptic plasticity. Synaptic plasticity is involved in learning and memory.
- FMR1 gene contains ‘CGG’ trinucleotide repeat. In normal condition, the number of CGG repeats range from 10-40. However, in Fragile X syndrome, the number of this repeat is more than 200 times which results in silencing of FMR1 gene and hence affect FMRP protein production. CGG repeat of around 45- 54 is called as grey zone and repeat of 55-200 is called pre-mutation. This pre-mutation is responsible for other two syndromes- FXTAS and FXPOI.
Symptoms of Fragile X syndrome
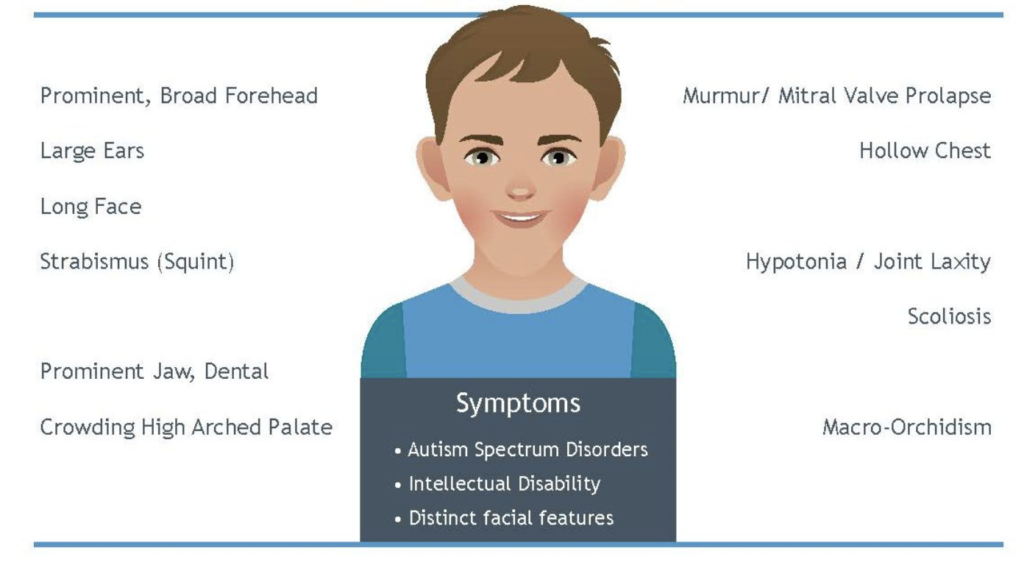
Figure- Some common physical features of fragile X syndrome (Source- Asuragen.com)
People with FXS may show following symptoms:
- They have difficulty in learning skills and may take longer time than normal to crawl, sit, walk, or speak.
- Impulsiveness
- Anxiety (general or social anxiety), depression.
- Obsessive compulsive behavior.
- Seizures.
- Autism symptoms.
- Hyperactivity
- Difficulty in paying attention, learning new skills, and picking up on social cues.
- Social issues like not liking being touched, not making eye contact, sensitive to crowd etc.
- Child may stutter.
Some children with FXS may show prominent physical features like:
- Long, narrow face with large head, large forehead, chin, and large ear.
- Crossed or lazy eyes.
- High- arched palate.
- Soft skin and loose joints.
- Flat feet.
- Low muscle tone.
- Boys may have enlarged testicles after puberty.
How common is Fragile X Syndrome?
- It affects around 1 in 5000-7000 men and 1 in 4000-6000 women. There is no exact data representing the number of people carrying fragile X premutation. Male or female with premutation act as carrier and have two times more chances of having baby with FXS than people without premutation.
- There is more risk of FXS in male than in female. And the symptoms are also more severe in male. Around 85% of males and 25 % of females with FXS show intellectual and developmental disability.
Diagnosis of FXS
- Blood sample is used by health workers for diagnosis of FXS. Diagnosis can also be done during pregnancy (prenatal test) in women who have FMR1 premutation or full mutation. Some prenatal testing used are amniocentesis (samples are taken from amniotic fluid) and chorionic villus sampling (samples taken form placenta). Prenatal testing is not very common and there is some risk to both mother and fetus.
- Most of the time parents notice first symptoms of delayed development in their baby. The average age at diagnosis is around 35- 37 month for boys and around 42 months for girls. Based on the symptoms, health care provider may suggest for diagnosis using blood of child for test called FMR1 DNA test.
Treatment of FXS
- Fragile X syndrome cannot be cured. Medicines can be used to prevent symptoms like seizures, or for behavioral disorder like anxiety, depression, or attention deficit disorder. Such medications include:
- Methylphenidate
- Guanfacine
- SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) like duloxetine, paroxetine.
- Supportive therapy may be helpful for child. Early intervention services may help to improve child’s intellectual development. Speech and language therapy is recommended for child in case of early diagnosis of FXS. Special accommodations at daycare or school is preferred.
- Occupational therapy can be helpful in performing daily activities.
Outlook for people with FXS
- FXS is not life-threatening condition. It doesn’t have any affect in life expectancy.
- According to a survey, around 9% of male and 44% of female with FXS are found to lead their life independently as adults.
Finding support
- To get more information about treatment, therapies, and intervention, one can contact National fragile X foundation at 1-800-688-8765 or email at treatment@fragileX.org.
References
- https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/gene/fmr1/
- https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/fragilex/conditioninfo/diagnosis
- https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/fxs/facts.html
- Sidorov MS etal. Fragile X mental retardation protein and synaptic plasticity. Molecular Brain volume 6, Article number: 15 (2013).
- Lozano R et al. Fragile X syndrome: A review of clinical management. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2016 Aug; 5(3): 145–157.