- Eplerenone is competitive aldosterone receptor antagonist which belongs to the class of potassium sparing diuretics. It is more selective for mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) than spironolactone– another aldosterone antagonist.
- It contains epoxy group which is responsible for its greater MR selectivity.
Indications of eplerenone
- To treat hypertension. It can be used in long term therapy of hypertension and congestive heart failure.
- Used in post myocardial infarction CHF (Congestive Heart Failure).
- It is weak diuretic and is used in combination with thiazide or loop diuretics to prevent excretion of K+ caused by other diuretics.
Mechanism of action of eplerenone
- Aldosterone is steroid hormone mainly synthesized in adrenal cortex but is also found in brain, heart and adipose tissues. It is an important regulator of sodium, potassium and water homeostasis. Aldosterone binds to specific mineralocorticoid receptor (MR). This MR-aldosterone complex translocates to nucleus and regulate expression of aldosterone induced proteins (AIPs) which stimulate Na+/K+ exchange sites.
- Eplerenone blocks mineralocorticoid receptor more selectively than spironolactone and inhibits binding of aldosterone to specific MR in distal part of nephron. This leads to inhibition of AIP synthesis and hence results in prevention of Na+ reabsorption and K+ and H+ secretion.
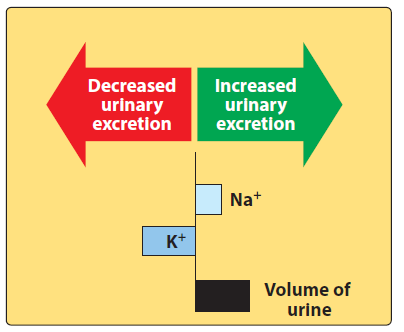
Figure- Change in urine composition induced by eplerenone (Source- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reveiws)
Effect on urinary excretion
- In most cases of edema, aldosterone level is high in blood which cause sodium retention. It antagonizes aldosterone and increases Na+ excretion and causes retention of K+. It has little or no effect on renal hemodynamics. The higher the level of endogenous aldosterone, the higher will be the effect of eplerenone on urinary excretion.
Pharmacokinetics of eplerenone
- It is well absorbed after oral administration and has significant plasma protein binding properties. It is metabolized to inactive metabolites by hepatic CYP3A4 and is eliminated.
- Its half-life is around 5 hours. It is excreted in urine and feces.
Adverse effects
- Since it has lower affinity for androgen and progesterone receptor, side effects like gynecomastia, menstrual irregularities, decreased libido and impotence are uncommon. The lower incidence of these endocrine side effects is its probable advantage than spironolactone.
- Life threatening hyperkalemia is major risk of eplerenone. It can cause other side effects like dizziness, GI intolerance, nausea, lethargy and mental confusion.
Drug Interaction
- The risk of hyperkalemia may increase when it is used in combination with other drugs that can induce hyperkalemia like ACE inhibitors and potassium supplements. Hence, it should be used with caution with such medications.
- Drugs which inhibit CYP3A4 like erythromycin, ketoconazole, itraconazole can increase plasma level of eplerenone and CYp3A4 inducers like carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin etc. may decrease its efficacy.
Contraindications
- Contraindicated in patients with hyperkalemia and who are at increased risk of developing hyperkalemia due to any disease or use of any medications.
- Used with caution in elder patients, patients with renal insufficiency and hepatic impairment.
- Avoided in patients with acid-peptic disease.
References
- Goodman and Gillman’s Manual of Pharmacology.
- Pharmacology and pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. 7th edition.
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1517/17425250902837973?journalCode=iemt20
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00700