
- Diuretics are the drugs used to increase urine flow and sodium excretion and are used in treating different medical conditions including hypertension, edema etc. Some commonly used diuretics include:
- Thiazide diuretics (chlorothiazide, hydrochlorothiazide)
- Potassium sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene)
- Osmotic diuretics (mannitol)
Screening methods of diuretics
There are different methods used for screening of diuretics which can be broadly classified into in-vivo and in-vitro methods.
In-vivo methods
- Diuretic activity in rats (LIPSCHITZ test)
- Clearance methods
- Stop flow technique
- Micro puncture techniques in rats
In-vitro methods
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibition invitro
- Patch clamp technique in kidney cells
- Perfusion of isolated kidney tubules
- Isolated kidney
Diuretic activity in rats (LIPSCHITZ test)
Purpose and Rationale
- Lipschitz et al described this technique in 1943 in which water and sodium excretion in test animal is compared with water and sodium excretion in rats treated with high dose of urea. It is one of the standard methods used for screening of diuretics.
Animals used
- Male wistar rats weighing about 100-200 gm. They are divided into test and standard group. Each group consist of 2 further group of 3 rats in each group.
Procedure
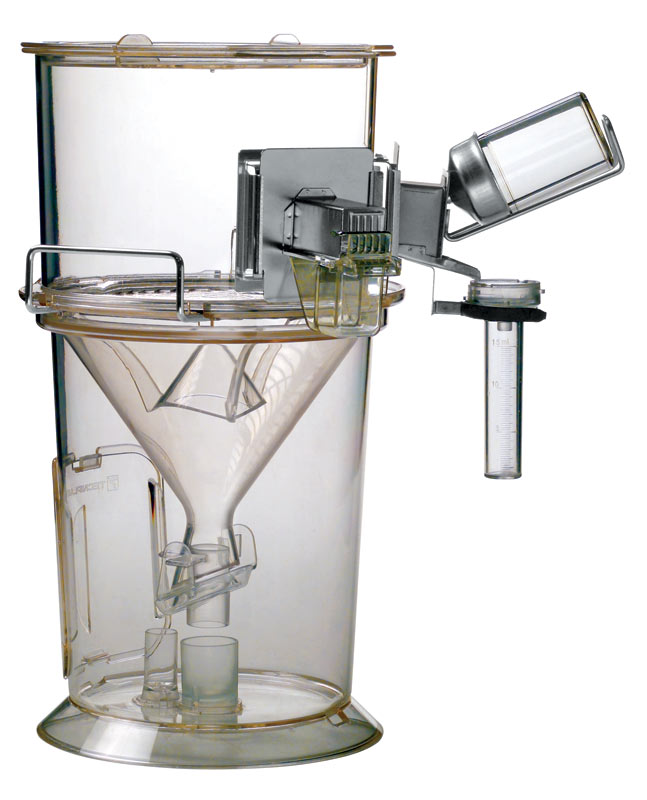

Figure- Metabolic cage used for LIPSCHITZ test (Source- Tecniplast.it)
- Rats are placed in metabolic cages which consist of wire mesh bottom and funnel to collect the urine. Funnel are provided with stainless steel sieves so that urine can pass, and feces remain retained. Three animals of a group can be put in one metabolic cage.
- Food and water are withdrawn fifteen hours before the experiment.
- Test group of animals receive experimental drug and std. group of animals receive 1 g/kg of urea via oral route or standard drug. After that 5 ml of 0.9% NaCl/100 gm body weight is also administered.
- Urine excretion is recorded after 5 and 24 hours.
Evaluation
- After certain time (5 hours and 24 hours), volume of urine excreted per 100 g body weight is calculated for both groups and results are expressed in term of LIPSCHITZ value.
LIPSCHITZ value= urine output in test animal / Urine output in std. drug or urea treated animal
- If LIPSCHITZ value ³ 1, it indicates positive effect of test compound and if LIPSCHITZ value> 2, it indicates potent diuretic effect.
- Sodium content in urine can be measured by using flame photometry.
Saluretic activity in rats
Purpose and rationale
- This method is used to measure saluretic property (excretion of electrolytes) of diuretics. It is the modification of above-described diuretic activity test in which excretion of potassium, chloride and osmolality is measured and determined in addition to water and sodium.
Procedure is same as in LIPSCHITZ test.
Evaluation
- Sodium and potassium level in urine is measured by flame photometry and chloride is measured argentometrically by potentiometrical end-point titration.
- The sum of sodium and chloride excretion gives saluretic activity of drug.
- For natriuretic activity we can use ratio Na+/K+.
Ratio value > 2 indicates favorable natriuretic effect.
Ratio value >10 indicates potassium sparing effect of compound.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibition is given by ratio Cl–/ (Na+ + K+).
Micro puncture technique in rats
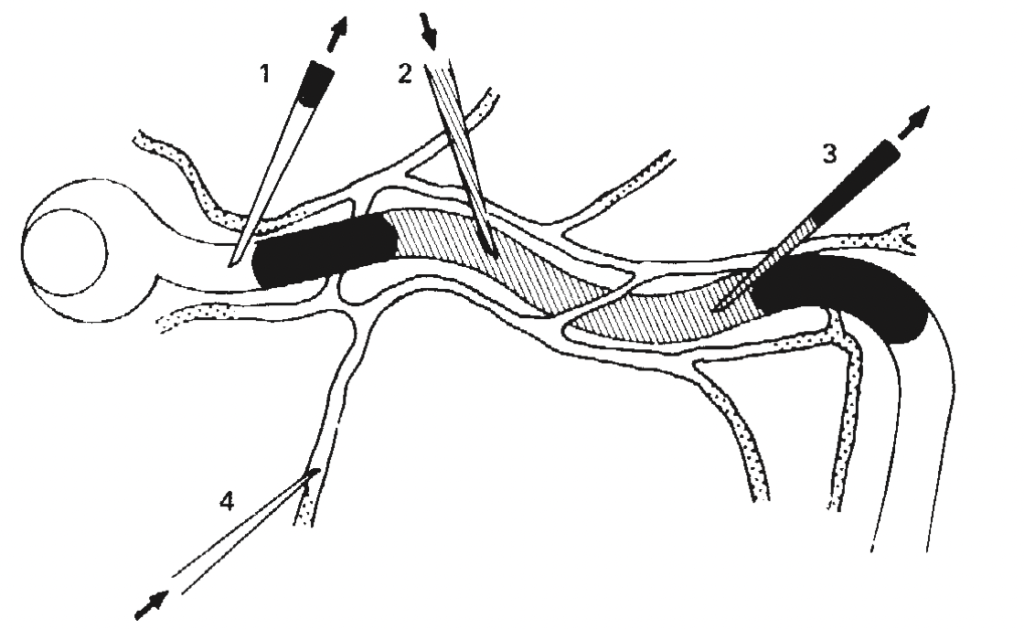
Figure- Schematic aspects of micro puncture technique (No. 1 indicate collection of tubule fluid by micropipette, 2 and 3 indicate continuous perfusion of tubules and 4 indicate method of perfusing peritubular capillaries). Source- Quamy et al, 1986.
Purpose and rationale
- Micropuncture techniques can be used to study the effect of test compound on single nephron. It particularly helps in determining localization of transport process within the nephron, hence helpful in accessing mechanism of action.
- This technique is used in rats due to accessibility of proximal and distal tubule and collecting tubule for micropuncture. It requires careful preparation of animal, meticulous collection of fluid samples and precise ultra-microanalyses.
Animals used
- Rats of any strain weighing around 250 gm.
Procedure
- Rats are kept in fasting for around 12-16 hours. Then they are anesthetized by using suitable anesthetic (e.g., intraperitoneal injection of thiopentone) and placed on thermostatically stable table.
- Tracheotomy is performed. Jugular vein and carotid artery are cannulated for collecting blood sample and infusing compounds respectively. Left kidney is exposed by flank incision and bathed with paraffin oil at 37 ° C. Ureter is cannulated to measure rectal temperature.
- Bolus injection of insulin 3H is administered which is followed by administration of 0.85% NaCl solution. Then after 45 minutes, controlled micro puncture of tubules is performed to collect fluid samples from proximal and distal tubule.
- Control period is followed by test period. After 30 minutes of equilibration period with test compound, micro puncture is performed again for collecting tubular fluid.
Evaluation
- Fluid sample is used to determine insulin clearance (GFR), fractional delivery of water, sodium and potassium level in urine and proximal and distal tubules and single nephron GFR.
References
- https://www.slideshare.net/jaineeljd007/diuretics-screening-models
- https://www.pharmatutor.org/articles/screening-diuretic-agents-overview
- Hailu W et al. Evaluation of the diuretic activity of the aqueous and 80% methanol extracts of Ajuga remota Benth (Lamiaceae) leaves in mice. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014; 14: 135.
- Quame G etal. Micropuncture techniques. Kidney International. 1986; 30: 152-165.
- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- Drug Discovery and Evaluation, Pharmacological Assay. 2nd edition.