
- Bleomycin is a family of natural glycopeptidic antibiotics fermented by Streptomyces verticillus. It is used as anti-neoplastic agent.
- It is available as generic medicine and is included in World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
Indications of bleomycin
- Used as antitumor agent against squamous carcinoma of cervix and testicular tumor.
- Used in Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- It is useful in epidermoid carcinoma of skin and upper respiratory passages.
- Its off-label is to treat various skin condition.
Mechanism of action of bleomycin
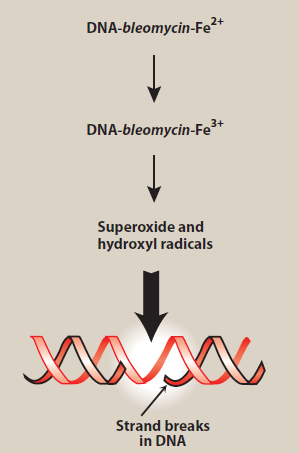
Figure- Mechanism of action of Bleomycin (Source- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews)
- It binds to DNA and form complexes with iron. The DNA-bleomycin- Fe2+ complex undergo oxidation to form bleomycin-Fe3+. During this oxidation, electrons are liberated which react with oxygen to form superoxide or hydroxy radicals. These radicals break DNA strand by acting on phosphodiester bonds of DNA.
- It also inhibits incorporation of thymine in DNA.
Resistance of bleomycin
- Resistance may occur due to increased concentration of bleomycin hydrolase causing it’s ncreased degradation of and glutathione S-transferase which causes bleomycin inactivation.
- It may be due to decreased uptake of drug, increased efflux of drug and DNA repair.
Pharmacokinetics
- It is administered though wide range of routes including IV, IM, subcutaneous or intrapleural route. And it can also be instilled into bladder for treatment of bladder cancer.
- It is mostly excreted unchanged in urine. Dose adjustment is required in renal patients. Its BBB (Blood Brain barrier) crossing capacity is poor. Its elimination half-life is around 3 hours.
- It is degraded by a specific hydrolase found in various tissues. Bleomycin inactivating enzyme (hydrolase) is less in tissues like skin and lungs and is more in tissues like liver and spleen. Hence, its toxic effects are more prominent in skin and lungs.
Adverse effects
- The common side effects include nausea, vomiting and alopecia. It can cause hypertrophic skin changes, hyperpigmentation, scleroderma like changes in skin and anaphylaxis like reaction/
- Pulmonary toxicity is serious side effect. It starts from rales, cough and lead to potentially fatal fibrosis. Pulmonary fibrosis caused by this drug is known as ‘bleomycin lung’. Pulmonary function test doesn’t predict early onset of this complication. It occurs in up to 46% of patients with a mortality rate of about 1-3%.
- Its myelosuppression effect is less.
Drug Interactions
- It can interact with drugs like brentuximab, phenytoin and drugs affecting kidneys like gentamicin and cisplatin.
- Decreases serum level of drugs like digoxin and phenytoin. It increases toxicity of cisplatin and radiotherapy.
Contraindications and warning
- Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to bleomycin and with pulmonary disease.
- All patients should have assessment of renal function before initiating this therapy. Careful physical monitoring of thorax and chest should be done after each cycle.
- It is contraindicated in pregnancy due to its harmful effect on fetus.
References
- Saitta P, Krishnamurthy K, Brown LH. Bleomycin in dermatology: a review of intralesional applications. Dermatol Surg. 2008; 34(10): 1299-313.
- Froudarakis M etal. Revisiting bleomycin from pathophysiology to safe clinical use. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 2013; 87: 90–100.
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bleomycin