
- Carmustine is an alkylating agent used as anti-neoplastic drug. It belongs to class of nitrogen mustard. Carmustine is β-chloro-nitrosourea compound (BCNU).
Uses of carmustine
- Used in treatment of brain tumor because of its ability to cross BBB (Blood Brain Barrier) including glioma, glioblastoma multiforme, medulloblastoma and astrocytoma.
- Occasionally used in treatment of lymphoma including Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- It is used in preconditioning for bone marrow transplant.
Mechanism of action of Carmustine
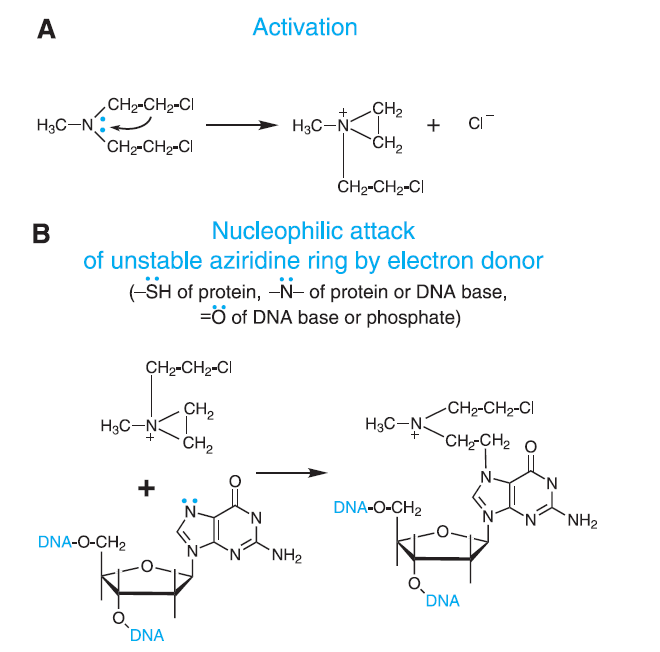
Figure 1- Mechanism of action of Alkylating agents (Source- Goodman and Gillman Book)
- It exerts its cytotoxic action in similar way to other alkylating agents. Alkylating agents form highly reactive quaternary ammonium derivatives (ethyleneimine cations). These intermediates covalently bind to groups like amino, phosphate and sulfhydryl of DNA bases. Alkylation of these bases make them unavailable for synthesis of DNA. Alkylation also lead to mispairing and repair causing breakage of DNA strand.
- It mainly causes alkylation at O6 guanine position. And it also causes crosslinking of DNA or with proteins and interfere with cell replication. It inhibits key enzymatic processes by causing carbamoylation of amino acids of proteins in targeted cells.
- Though it alkylates DNA in all phases, cytotoxic effect is more in rapidly dividing cells.
Pharmacokinetics of Carmustine
- It is administered though IV route and as chemotherapy wafer implants. An implantable carmustine wafer is used as supplementation with surgery and radiation in newly diagnosed malignant glioma and as adjunct with radiation in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. After IV infusion, it disappears from plasma with variable half-life of 15-90 minutes.
- It is lipid soluble and can cross BBB. Its CSF (Cerebrospinal Fluid) concentration is 15-30 % of concurrent plasma concentration value. Due to lipophilicity, it is distributed widely throughout the body.
- It undergoes extensive metabolism in liver. It is mainly excreted through renal route in the form of urine.
Adverse Effects
- It can cause delayed and prolonged myelosuppression. Blood count is monitored weekly for at least 6 weeks after each dose. It is highly carcinogenic and mutagenic.
- When used in high doses, it can cause pulmonary fibrosis, renal fibrosis and secondary leukemia.
Contraindications
- Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to carmustine.
- Contraindicated in pregnancy and breast feeding.
- Should be used with caution in patients with hepatic impairment and renal impairment.
References
- Xiao Z et al. Carmustine as a Supplementary Therapeutic Option for Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Neurol. 2020.
- Clinical Neurotoxicology Syndromes, Substances, Environments. 2009. 69-87.
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.