- Ethosuximide is a class of antiepileptic drug. It is most frequently used succinimide which came into medical use since about 1960.
- It is available both as brand and generic medicine. Ethosuximide is included in World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
Indications of Ethosuximide
- Ethosuximide is FDA approved to treat absence seizures. It is used as first choice to treat absence seizures. Absence seizures is a condition characterized by sudden impairment consciousness without impulsive movement and without loss of postural control. It is not effective in partial and tonic-clonic seizures.
- It can be used in combination therapy for patients who are suffering from both absence and other kind of seizures.
Mechanism of action of Ethosuximide
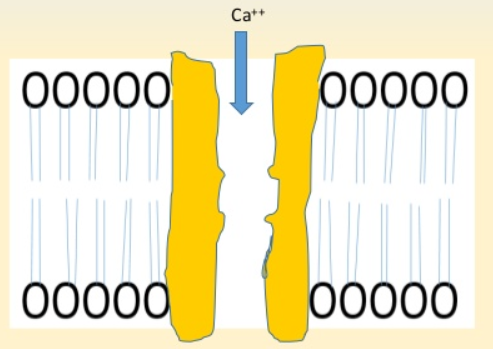
Figure- Ethosuximide inhibits type T calcium cannel
- It reduces low threshold calcium current (T current) in thalamic neurons responsible for generation of absence seizures. It modulates thalamic 3-Hz spike and z activity and reduces propagation of abnormal electrical activity in brain.
Pharmacokinetics of Ethosuximide
- It is well absorbed after oral administration, does not bind to plasma proteins and is distributed through body water. It is present in plasma mostly in free form.
- Peak plasma level reaches within 3-5 hours. Its half-life is about 30-40 hours in children and 50-60 hours in adults.
- It is eliminated primarily by metabolism. It is metabolized in liver. Only about 20% of administered drug is recovered unchanged in urine.
Adverse effects
- Common side effects are GI problems (nausea, vomiting, anorexia) and CNS effects (drowsiness, dizziness, lethargy, headache).
- Some rare side effects include skin rashes, SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematous), psychic disturbance, Parkinson like symptoms, anxiety, hallucination and paranoia.
- It also carries a very small risk of blood abnormalities including thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, eosinophilia and aplastic anemia.
Contraindications and warnings
- It should be used with caution in people with liver disease, blood dyscrasias and kidney disease.
- Ethosuximide can cause birth defects if used by pregnant woman. It should be used during pregnancy only if its benefits outweigh the risk. It passes through the milk during breastfeeding. Consultation of doctor is needed for use of ethosuximide in pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- It is not used in children less than 3 years of age.
- It should not be withdrawn abruptly as it may increase risk of seizures. Should be withdrawn slowly with caution.
- Person involved in driving vehicles or operating machines should be extra cautious as it causes sleepiness.
Drug Interactions
- Ethosuximide increases the level of drug like phenytoin. Drugs like valproic acid increases the level of ethosuximide.
- Concurrent administration with alcohol increases chance of dizziness or sleepiness so patient should be warned about it.
Preparation and Dosage
- It is available as 250 mg capsules and syrup (250 mg/5 ml). The initial preferred dose is 250 mg in children and 500 mg in adults. The dose can be increased by 250 mg weekly until seizure is controlled.
- The maximum daily dose is 750-1000 mg.
References
- Handbook of Clinical Neurology. 2014; 119: 417-432
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics book. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman’s Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics