
What is respiratory system?
- Respiratory system is the important system of our body which helps us to breathe. This system consists of:
- Nose and nasal cavity
- Mouth
- Sinuses
- Pharynx (throat)
- Larynx (Voice box)
- Trachea (windpipe)
- Diaphragm
- Lungs
- Bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli
- Blood capillaries
- The main function of respiratory system is involvement in breathing during which there is exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Other functions include help in talking and smelling, removal of toxic gases including carbon dioxide and protecting airway from harmful and irritant substances.
Respiratory diseases
- Respiratory diseases are common problem all over the world. Acute and chronic respiratory diseases are leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Some factors which increase risk of respiratory infections smoking, pollution and genetic involvement.
- Some common diseases of respiratory system are-
Asthma (one of the chronic respiratory diseases)
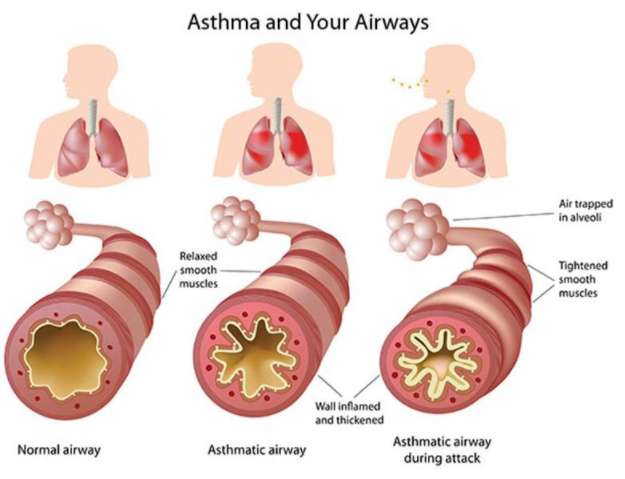
Figure – Effect of asthma in airways
- Asthma is an inflammatory disease which affect our lungs. The narrowing of bronchi can cause increased resistance to air flowing through it leading to symptoms like wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath and persistent coughing. Triggering agents of asthma may be allergic reaction, infections and pollutants.
- Asthma may be minor issue in some patients whereas in some cases, it may interfere with daily activities and may be life-threatening. It is not possible to cure asthma completely, but various pharmacological drugs are available which help to control its symptoms. Various types of drugs which has been used to treat asthma include;
- β-2 adrenergic receptor agonist (examples- salbutamol, terbutaline, fenoterol)
- leukotriene modifiers (example- montelukast)
- glucocorticoids
- aminophylline etc.
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)

Figure- Normal lungs and lungs with COPD
- COPD is clinical terms used for a group of pathological conditions in which there is complete or partial obstruction of airflow at any level from trachea to smallest airway. The main physiological abnormality is accelerated rate of decrease in Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV) compared to normal. Other symptoms include cough, sputum production, wheezing and difficulty in breathing. COPD is not reversible like asthma. In most cases, asthma occurs along with COPD. It is generally associated with smoking.
- Two types of COPD are emphysema and chronic bronchitis. The major feature of emphysema is inflation and destruction of alveoli whereas inflammation of the lining of bronchial tubes is major charcteristic feature of chronic bronchitis tubes. COPD cannot be cured but can be treated. Its treatment is somewhat similar as of asthma. The treatment strategy includes:
- Inhaled bronchodilator and glucocorticoids
- Oxygen inhalation
- Prophylactic antibiotics.
Pneumonia
- It is an acute inflammation of lung parenchyma and is caused by infection in air sacs of lungs. The infection may be bacterial, viral or fungal. Symptoms include cough, fever, shortness of breath and shaking chills. The symptoms are severe in very young and very old patients. the mortality rate due to pneumonia is 10 -12 folds greater in such patients than in adults.
- Pneumonia is classified based on where patient is infected. It may be community acquired (outside hospital or healthcare facilities), hospital acquired (patient get infected while staying in hospital for other illness), health- care acquired (patients get infected in long-term care facilities or out- patient clinic) and aspiration pneumonia (occurs when we inhale food, drink or saliva into lungs). The treatment may differ according to causative agent. Bacterial pneumonia is usually treated by using antibiotics.
Lung cancer
- It has many forms and may occur in any part of lungs. However, it mostly occurs in main part of lung, in or near air sacs. It is one of the leading causes of cancer death worldwide. Two main types of lung cancer are small cell lung cancer and non- small cell lung cancer. Smoking is the major cause of lung cancer, but it also occurs in person who doesn’t smoke.
- Signs and symptoms are prevalent only in advanced stage. This includes
- Cough which doesn’t go away and blood in cough
- Shortness of breath
- Weight-loss
- Chest- pain
Cold (Viral respiratory diseases)
- Common cold is viral infection of upper respiratory tract. Symptoms may appear one to three days after exposure to cold causing virus. People may recover from common cold within 7- 10 days. Signs and symptoms may vary from person to person and may include:
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Sneezing
- Body ache and headache
- Fever.
Cystic Fibrosis
- It is genetic respiratory disease. However, it also affects digestive system. It’s main feature is defective gene which makes body to produce thick and sticky mucus which can clog lungs and pancreas.
- The signs and symptoms may vary person to person which include
- Repeated lung infections
- Persistent cough and thick mucus production
- Exercise intolerance
- Foul smelling and greasy stool
- Constipation.
Additional respiratory disease- COVID-19
- COVID-19 is new respiratory illness caused by a family of viruses called coronaviruses. It spread mainly from person to person. The primary symptoms include cough, fever, new loss of smell or taste and shortness of breath.
- It can infect upper and lower part of respiratory tract.
References
- Lung cancer – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/what-is.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK11773/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cystic-fibrosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353700
- https://www.unitypoint.org/homecare/article.aspx?id=2448b930-1451-43e4-8634-c0c16707c749