- Depression is one of the common psychiatric diseases which is characterized by various symptoms including low self-esteem, feeling of hopelessness and worthlessness, depressed mood, and irritability.
- Some classes of drug which can be used in management and treatment of drug include:
- SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor). E.g., Sertraline, Fluoxetine, Paroxetine.
- SNRIs (Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors). E.g., Venlafaxine, Duloxetine.
- MAO inhibitor. e.g., Selegiline, Isocarboxazid.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants. E.g., Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline.
Screening of Antidepressants
Various screening model of Anti-depressants include:
Behavioral Test for screening of anti-depressants
- Despair Swim Test
- Catalepsy Antagonism in chicken
- Tail suspension test in mice
- Learned helplessness in rats
- Muricide behavior in rats
- Behavioral change after neonatal clomipramine treatment
In-vitro methods for screening of anti-depressants
- Inhibition of 3H- norepinephrine uptake in rat brain synaptosomes
- Inhibition of 3H- dopamine uptake in rat striatal synaptosomes.
- Binding to monoamine transporters.
- Inhibition of 3H- serotonin uptake in synaptosomes.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibition in rat brain synaptosomes.
- Receptor sub sensitivity after treatment with antidepressants.
- Measurement of beta-adrenoreceptor stimulated adenylate cyclase.
Test for antidepressant activity based on the mechanism of action
- Compulsive gnawing in mice.
- Apomorphine induced hypothermia in mice.
- Reserpine induced hyperthermia.
- Serotonin syndrome in rats.
- Sexual behavior in male rats.
- Potentiation of norepinephrine toxicity.
- Tetrabenazine antagonism in mice.
Despair swim test/ Forced Swim Test
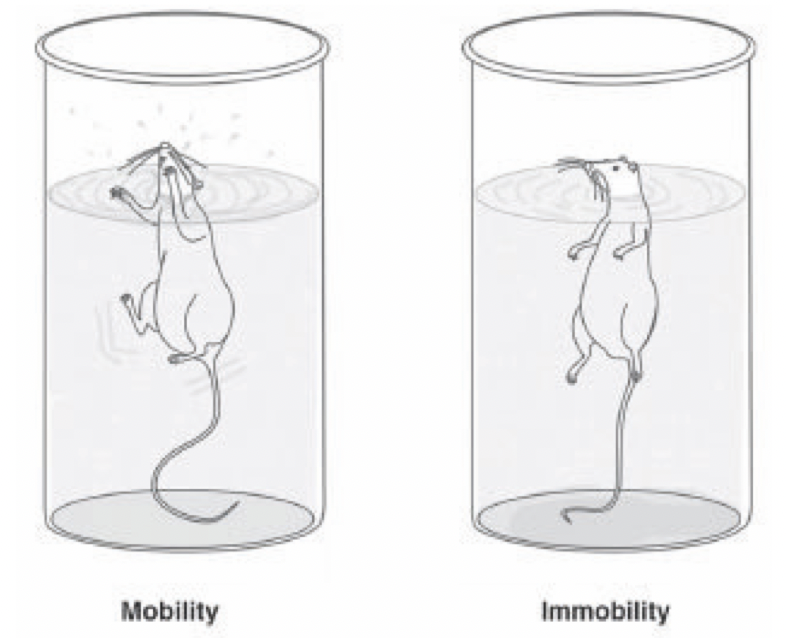
Figure- Schematic representation of mobility and immobility in FST- one of the method for screening of anti-depressants (Source- Kedzierska etal, 2016)
Purpose and Rationale
- Porso et al. introduced this model which has become one of the most commonly used screening model of anti-depressants.
- Mice and rats when forced to swim in restricted space from which they are unable to escape, develop immobility which indicate state of despair. Agents which are effective in depression can reduce such state of despair.
Animals used
- Male Sprague Dawley rats (160-180 gm).
Procedure
- Animals are placed in inescapable cylinder filled with water. In beginning, rats try to escape by swimming actively and trying to climb the wall or dive to bottom which decreases slowly. After 5-6 minutes, they remain in immobile state for around 80% of the time. Immobility is characterized by animals floating passively in water in upright and slightly hunched position with nose just above the surface.
- After 15 minutes of putting in water, rats are taken out from water, dried and returned to their cages. After 24 hours, the test is performed again for 5 minutes, and immobility is measured.
- Rats are administered with standard drug or test compound one hour before performing test and immobility is measured.
Evaluation
- Duration of immobility is measured and compared between controls and test group. We can also evaluate dose-response.
Pros and cons
- Some of its pros include low cost, simple to conduct, fast and reliable and wide range of applications.
- Cons include its poor face and construct validities. And also, there are chances of false positive results for compounds like amphetamine and caffeine which increase the general activity.
Tail suspension test

Fifure- Schematic representation of mobility and immobility in tail suspension test- one of the method for screening of anti-depressants (Source- Kedzierska etal, 2016)
Purpose and rationale
- Steru etal. Proposed this method in 1985. The theory behind this test is like that of forced swim test. It is also commonly used screening model of anti-depressants.
Animals used
Male balb/cJ mice (weighing 20-25 gm)
Procedure
- In this test, mice are suspended by using adhesive tape on tail (1 cm from the tip of tail) on the edge of shelf or horizontal bar which is 58 cm above a tabletop.
- At first, the animals are highly active which slowly decreases, and animals develop unavoidable stress. As a result, they become immobile. Immobile state is characterized when animals hang passively and completely motionless for at least 1 minute. Immobility duration is measured for 5-6 minutes.
- Animals are divided in two group: control and test group. Standard and test compound is administered 30 minutes before test.
Evaluation
- Duration of immobility is measured and compared. Percentage of animals showing immobility is also counted and compared among control and test group.
- ED50 value is calculated.
Pros and cons
- Pros are it is inexpensive and simple method. It can detect broad spectrum of antidepressants.
- Cons are it helps to measure acute effect of antidepressants but not chronic effect.
References
- Kedzierska E et al. Using tests and models to assess antidepressant-like activity in rodents. Curr. Issues Pharm. Med. Sci. 2016; 29(2): 61-65.
- Steru L etal. The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1985; 85(3): 367-70.
- https://www.slideshare.net/VMMCSJH/screening-of-antidepressant
- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- Drug Discovery and Evaluation, Pharmacological Assay. 2nd edition.