- Posaconazole is triazole antifungal agent. It is chemically related to itraconazole. It is a second generation, synthetic triazole and has broad spectrum antifungal agent.
- Posaconazole got its FDA approval for medical use in 2006. It is also available as generic medicine.
Indication of posaconazole
- Used in prevention and treatment of invasive fungal infections by Candida species and Aspergillus species in severe immunocompromised patients.
- Used to treat oropharyngeal candidiasis including oropharyngeal candidiasis that doesn’t respond to fluconazole or itraconazole.
- It is preferred than amphotericin-B as drug of choice in treating zygomycete infection.
Mechanism of action of posaconazole
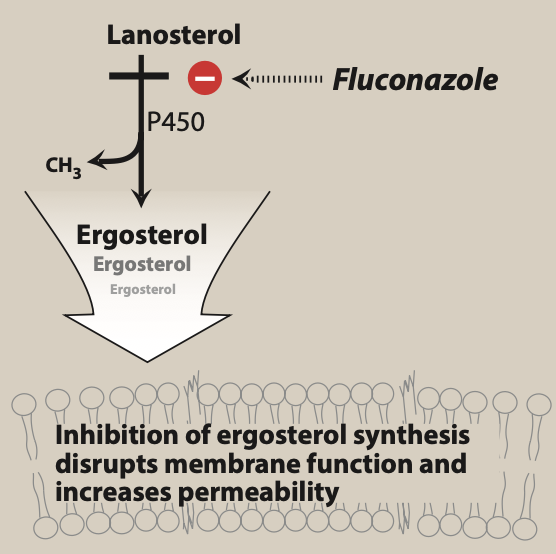
Figure- Mechanism of action of triazole antifungal agents including Posaconazole (Source- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews, Pharmacology, 6th edition)
- Its mechanism of action is similar to other triazole antifungal agent. It also works by inhibiting ergosterol synthesis.
- Ergosterol is major component of cell membrane of fungi. It binds to heme cofactor located on fungal cytochrome P450 enzyme, C-14 a-demethylase which is involved in 14- alpha demethylation reaction of lanosterol to ergosterol and inhibit the enzyme. This inhibition in ergosterol synthesis cause impairment in membrane structure and function and results in inhibition of fungal cell growth.
Pharmacokinetics of posaconazole
- It is available as oral tablet, oral suspension or IV formulation and is also available as delayed release oral tablet which was approved in 2013. It has low oral bioavailability which can be increased by administering with food.
- Posaconazole has long half-life (around 25-31 hours). Though it has long half-life, its suspension form is given in divided doses throughout the day because of its saturable absorption in gut. It is highly protein bound (around 99%). It mostly binds to protein albumin and large volume of distribution.
- Unlike other azole antifungal agents (itraconazole, voriconazole), it is not metabolized by CYP450 enzymes. It undergoes glucuronidation in liver. Most of the drug is excreted via fecal route.
Adverse effects
- It is generally well tolerated drug. Adverse effects include GI disturbances like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and GI upset. It can also cause neutropenia and elevation in serum hepatic transaminase level.
- IV infusion may cause thrombophlebitis.
Drug Interaction
- Posaconazole inhibits CYP3A4 and p-glycoprotein which is the reason for its numerous drug- drug interaction. It can increase plasma concentration of drugs which are substrates of CYP3A4 like cyclosporin and tacrolimus and can lead to toxicity.
- Co-administration of Posaconazole with many CYP3A4 substrates including risperidone, pimozide, atorvastatin, quinidine and ergot alkaloids are contraindicated.
- Drugs like cimetidine, PPIs (proton pump inhibitors) which affect gastric pH may decrease absorption of oral posaconazole.
Contraindications
- Contraindicated in patient hypersensitive to posaconazole or any other ingredients of the preparation.
- Its use with drugs like pimozide, risperidone, atorvastatin and quinidine is contraindicated.
References
- Chen L et al. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Posaconazole. Drugs. 2020; 80: 671–695.
- Moore jn et al. Pharmacologic and clinical evaluation of posaconazole. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015 May; 8(3): 321–334.
- Bhattacharya M et al. Posaconazole. Drug Review. 2010; 56(2): 163-167.
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01263
- A textbook of Clinical Pharmacology and therapeutics. 5th edition.
- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology. 6th edition.
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.