- Alteplase is a recombinant form of human tissue plasminogen activator. It is produced by recombinant DNA technology from human tissue culture. Chemically, it is similar to endogenous tissue type plasminogen activator.
- It is thrombolytic agent and is more effective compared to streptokinase. It is expensive.
Indications of alteplase
- Used in emergency treatment of myocardial infarction.
- Used in treating ischemic stroke and pulmonary embolism.
- Its off-label uses is catheter directed thrombolysis in treatment of peripheral arterial occlusive disease and deep vein thrombosis.
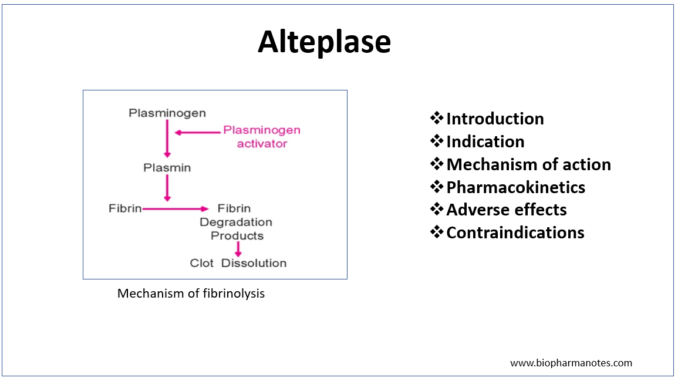
Mechanism of action of alteplase
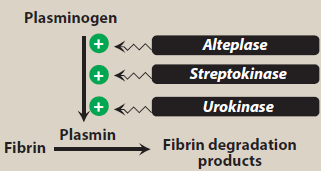
Figure- Activation of plasmin by thrombolytic agents (Source- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews)
- Like other fibrinolytic agents, it also acts as plasminogen activator. Plasminogen is inactive proteolytic enzyme present in plasma which is converted to plasmin by plasminogen activator. The plasmin formed is needed to breakdown fibrin which is major component of blood thrombus. This results in dissolution of blood clot.
- Alteplase binds to fibrin rich clots via Kringle 2 domain and fibronectin finger-like domain. The protease domain if alteplase cleaves ARg/val bond of inactive plasminogen leading to formation of plasmin. The plasmin formed binds with fibrin and degrades fibrin clots, fibrinogen and other plasma proteins resulting in dissolution of blood clot.
- It has some specificity for fibrin bound plasminogen. Hence, its effect on circulating fibrinogen is only about 50%.
Pharmacokinetics of alteplase
- It is available as lyophilized powder in 50 mg and 100 mg vials. It is administered through IV route. Its dose may vary depending on its purpose. For catheter clearance, it is instilled directly into catheter.
- Its plasma half-life is 4-8 minutes. Because of its short half-life, it is administered slowly by iv infusion and may require co-administration of heparin.
- It is cleared by liver. It is inactivated by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI1).
Adverse effects
- Its major side effect is bleeding. This risk is high in patients with conditions like major surgery, cerebrovascular disease, recent intracranial hemorrhage, uncontrolled hypertension, ophthalmic conditions.
- Other side effects include fever, anaphylaxis and angioedema.
Contraindications
- Contraindicated in patients with bleeding disorder like internal bleeding, subarachnoid hemorrhage and intracranial hemorrhage.
- Contraindicated in patients with stroke within last three months, intracranial or intraspinal surgery within last three months.
- It is pregnancy category C drug which means more research about its effect on pregnancy had not been done.
- It is contraindicated in patients with severe uncontrolled hypertension.
- Contraindicated in intracranial neoplasm, arteriovenous malformations.
- Contraindicated in patients with severe head trauma within last three months.
References
- Wagstaff et al. Alteplase. A reappraisal of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in vascular disorders other than acute myocardial infarction. Drugs. 1995 Aug;50(2):289-316.
- Dhillon S. Alteplase: a review of its use in the management of acute ischemic stroke. CNS Drugs. 2012; 26(10): 899-926.
- A Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00009
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499977/