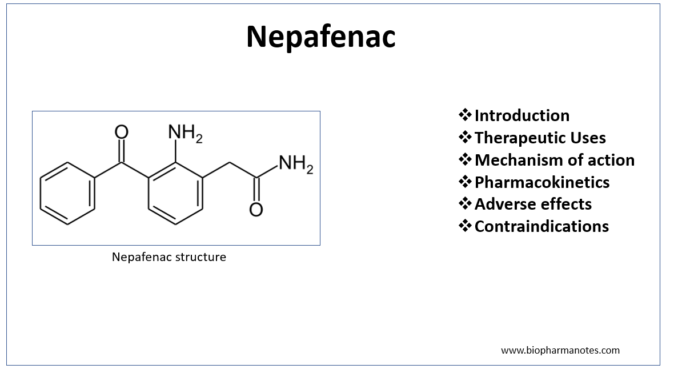
- Nepafenac is non-steroidal anti- inflammatory drug (NSAIDs) which is available as prescription eye drops. It is a member of new class of NSAID prodrugs for ophthalmic use with novel drug delivery mechanism.
- Nepafenac received US FDA priority approval on August 19, 2005. Chemically, it is 2- amino-3- benzoylbenzeneacetamide.
Indications of Nepafenac
- It is approved to treat pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery in United States, Europe and other countries. It should be administered to patient one day before surgery, on the day of surgery and upto 14 days of surgery. An extra dose is required 30-120 minutes before surgery.
Surgical trauma produced during cataract surgery causes activation of COX-1 and COX-2 which produce prostaglandins from arachidonic acid. Prostaglandins produced result in inflammation, pain and discomfort after surgery.
- In Europe, it is indicated for reducing risk of postoperative macular edema associated with cataract surgery in diabetic patients. In patients with diabetes, cataract surgery may be followed by postoperative macular edema which is one of the major causes for suboptimal visual outcomes.
Mechanism of action of Nepafenac
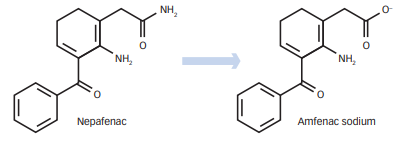
Figure 1 – Conversion of Nepafenac (prodrug) to amfenac (active form) (source- Nardi et al, 2012)
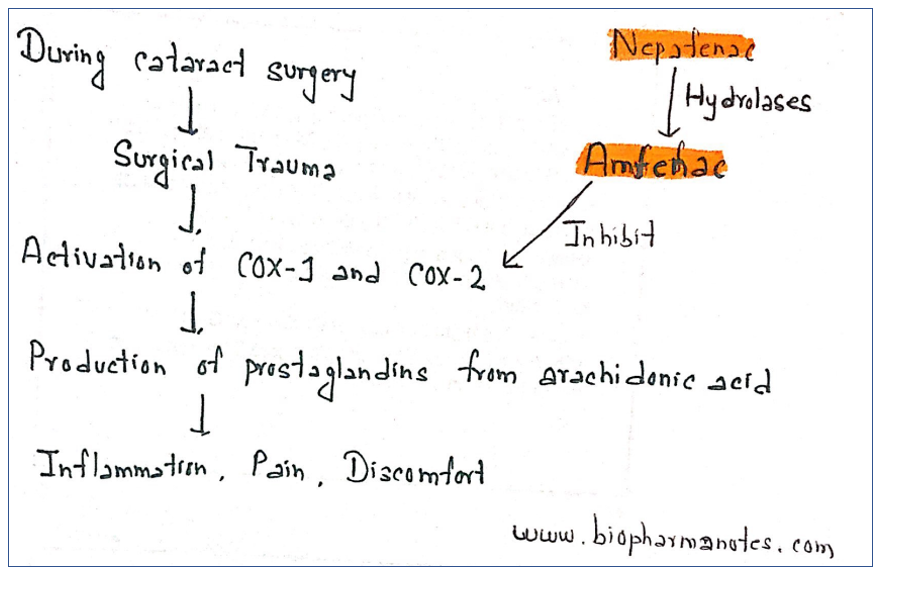
Figure 2- Mechanism of action of Nepafenac
- Nepafenac is prodrug which is deaminated to its active from amfenac. After its administration, it penetrates cornea where it is deaminated by intraocular hydrolases. Amfenac causes potent inhibition of COX 1 and COX 2 enzymes, enzymes required for prostaglandin production. Nepafenac also exhibits some COX inhibition.
Pharmacokinetics
- Available as 0.1% and 0.3% ophthalmic suspension. After administration, it rapidly crosses cornea. It crosses cornea 6 times faster than diclofenac in vitro. Its rapid crossing capacity is due to its molecular structure. Nepafenac’s structure doesn’t possess any charge whereas other NSAIDs available possess acidic charge.
- Its high bioavailability in posterior segment of eye acts as continuous source of amfenac and is responsible for its prolonged action in ocular tissues.
- It has rapid onset of action, produces action within 15 minutes of administration. Its duration of action is 8 hours after topical ocular administration and shows peak action at 30 minutes.
- It is deaminated to amfenac by intraocular hydrolases in ciliary body epithelium, choroid and retina. Amfenac undergoes extensive metabolism to more polar metabolites involving hydroxylation of aromatic ring. This leads to formation of glucuronide conjugates.
Adverse effects
- In clinical trials, nepafenac is proved to be safe. Some non-serious adverse events are there which can be resolved with or without treatment. Commonly reported adverse events were capsular opacity, visual acuity, increased IOP (intraocular pressure) and sticky sensation.
- In 3% of patient with diabetes, prolonged use may cause punctuate keratitis. Other side effects include runny nose, headache, slow or delayed healing.
Contraindications
- Contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to NSAIDs including aspirin.
- Use of soft contact lenses while using nepafenac should be avoided as preservative present in nepafenac eye drops can be absorbed by lenses.
- Its safety data in pregnancy and breastfeeding women are not available. So its use is not favored in such case.
References
- Chastian et al. Distribution of topical ocular nepafenac and its active metabolite amfenac to the posterior segment of the eye. Exp Eye Res. 2016 Apr; 145: 58-67.
- Singh et al. Efficacy of nepafenac ophthalmic suspension 0.1% in improving clinical outcomes following cataract surgery in patients with diabetes: an analysis of two randomized studies. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017; 11: 1021–1029.
- Nardi M. Nepafenac in the Prevention and Treatment of Ocular Inflammation and Pain Following Cataract Surgery and in the Prevention of Post-operative Macular Oedema in Diabetic Patients. European Ophthalmic Review. 2012; 6(3): 169-172.
- Bottos et al. Pharmacology, clinical efficacy and safety of nepafenac ophthalmic suspension. Expert Review of Ophthalmology. 2008; 3(2).
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB06802
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathway/PathBank:SMP0000702
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5768593/