- Chlorambucil is an aromatic nitrogen mustard derivative. It is a bifunctional alkylating agent and is commonly used chemotherapeutic agent.
- It was first synthesized by Everett et al. Chlorambucil was approved by FDA in 1957. It is included in World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
Indications of chlorambucil
- It is preferred drug to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
- Used to treat Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
- Used to treat lymphosarcoma, giant follicular lymphoma and Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia.
Mechanism of action of chlorambucil
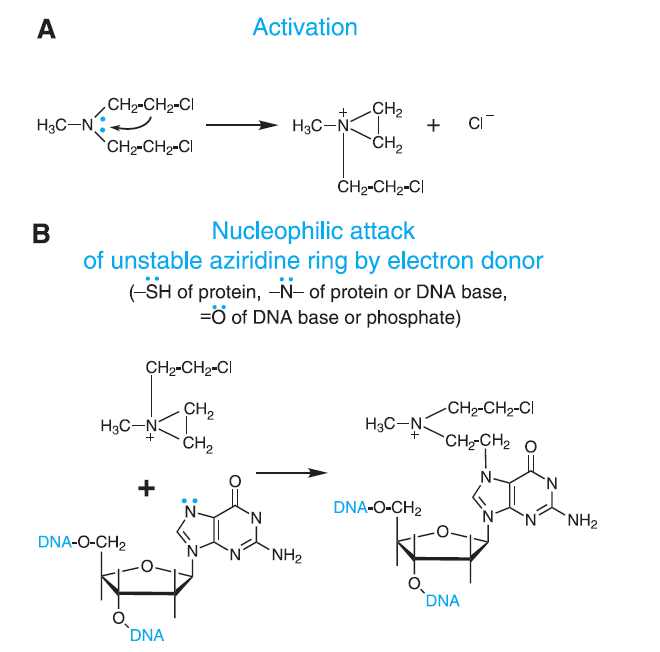
Figure 1- Mechanism of action of Alkylating Agents (Source- Goodman and Gillman Book)
- Like other alkylating agents, it can transfer alkyl group to suitable receptor. Alkylating agents from highly reactive quaternary ammonium cation (ethyleniminium cation) which can alkylate groups like amino, phosphate and sulfhydryl. Hence, it alkylates DNA at guanine N-7 position and form DNA-DNA cross links. It can form both intra- and inter strand DNA cross links and DNA-protein cross links. It leads to inhibition of DNA synthesis and hence cause cell apoptosis.
- Chlorambucil is a non-phase specific cytotoxic agent.
Pharmacokinetics of chlorambucil
- It is the shortest acting among nitrogen mustard. It is administered through oral route. Oral absorption is reliable and adequate as it is rapidly and completely absorbed from GI tract.
- It extensively binds to plasma and tissue proteins. Metabolism takes place in liver and is metabolized in liver to phenlacetic acid mustard. It is almost completely metabolized leading to extremely low urinary excretion. Its plasma half-life is around 1.5 hours.
Preparation and Dosage
- It is available as 2 mg tablets.
- The usual dose is 0.1-0.2 mg/kg of body weight daily for 3 to 6 weeks. Maintenance therapy of 2 mg /day is required to maintain clinical remission.
Adverse Effects
- It is considered less toxic than other nitrogen mustards. It doesn’t possess local irritant property and chances of alopecia is less even after prolonged use.
- Chlormbucil causes myelosuppression. Its myelosuppressive effect is dose-dependent and reversible. It can cause anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia and pancytopenia.
- Chlorambucil is carcinogenic, mutagenic and teratogenic. It can cause sterility and permanent azoospermia in adult males and amenorrhea in female.
Contraindications
- It should not be used in patients hypersensitive to chlorambucil. There may be chances of cross-sensitivity between chlorambucil and other alkylating agents.
- It is pregnancy category D drug. It is contraindicated in pregnancy as it causes fetal harm when administered to pregnant woman.
- Due to its carcinogenic property, it should not be given to patients other than with chronic lymphatic leukemia and malignant lymphoma.
References
- LEUKERAN® (chlorambucil)Tablets (nih.gov)
- Chlorambucil | DrugBank Online
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.