- Etoposide is semi-synthetic derivative of podophyllotoxin obtained from plant Podophyllum peltatum. It is an anti-neoplastic agent used to treat different kinds of cancer.
- Etoposide is included in World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines. It was first synthesized in 1966. It was introduced for medical use in 1971.
Indications of Etoposide
- Used in treatment of lung cancer, germ-cell tumor and Kaposi’s sarcoma associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
- To treat non- Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Used in combination with bleomycin and cisplatin for testicular carcinoma.
Mechanism of action of Etoposide
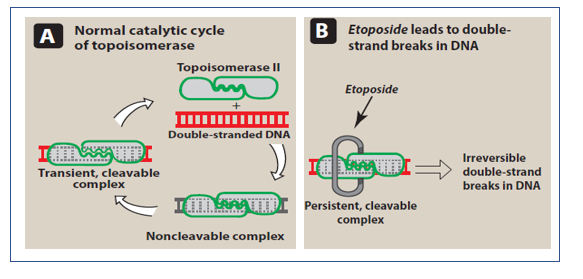
- It is phase-specific cytotoxic drug which blocks cells in late S to G2 phase of cell cycle. Its major target is topoisomerase II. Topoisomerase II forms transient break in double strand DNA to manage DNA tangles and supercoils which is followed by resealing of the transient break.
- They form complex with topoisomerase II and DNA and prevent resealing of the DNA break. The enzyme remains bound to free end of broken DNA strand which results in transient, cleavable form of complex. This is susceptible to irreversible double strand DNA break. Hence, there occurs accumulation of double strand DNA break and cell death.
Pharmacokinetics of Etoposide
- It is administered by oral or IV route. It is rapidly absorbed after IV administration and moderately absorbed after oral administration. The bioavailability of oral etoposide is around 50%. Its absorption is not linear with increasing oral dose within clinical range.
- It crosses blood brain barrier. The drug concentration in CSF (Cerebrospinal Fluid) is about 1-10% of that in plasma. It is metabolized in liver to its metabolites. Around 40% of administered drug is excreted in the form of urine.
Adverse effects
- The primary acute toxic effect is myelosuppression. Leukopenia is dose-limiting toxicity. Thrombocytopenia may occur sometimes and is less severe.
- Alopecia is common and reversible. Other side effects include nausea, diarrhea, stomatitis, phlebitis, fever and allergic reactions.
Drug Interaction
- When used in combination with warfarin, it increases prothrombin time.
- Concurrent administration with other cytotoxic agents shows synergistic effect.
Contraindications
Contraindicated in following conditions:
- In patients who are hypersensitive to this drug.
- Patients with hepatic dysfunction, bone marrow depression.
- In pregnancy and breastfeeding mothers.
References
- Selvin ML. The clinical pharmacology of etoposide. Cancer. 1991; 67(1 Suppl): 319-29.
- Slevin ML, Clark PI. The Clinical Pharmacology of Etoposide and Teniposide. Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 1987; 12: 223-252.
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557864/