- Selegiline is selective and irreversible MAO-B (Mono Amine Oxidase) inhibitor. It is used to treat Parkinson’s disease and depression.
- Selegiline is 1st selective MAO-B inhibitor synthesized in 1965 by Knoll and Magyar. Chemically it is R-optical enantiomer of deprenyl (phenyl-isopropyl-methyl-propargylamine).
Indications of selegiline
- FDA approved for use as additional treatment in Parkinson’s disease. It can be used with levodopa to enhance actions of levodopa, decreases ‘wearing effect’ of leveodopa and to reduce the dose of levodopa.
- Used in treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD).
- Its off label uses include treatment of early Parkinson’s disease and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Mechanism of action of selegiline
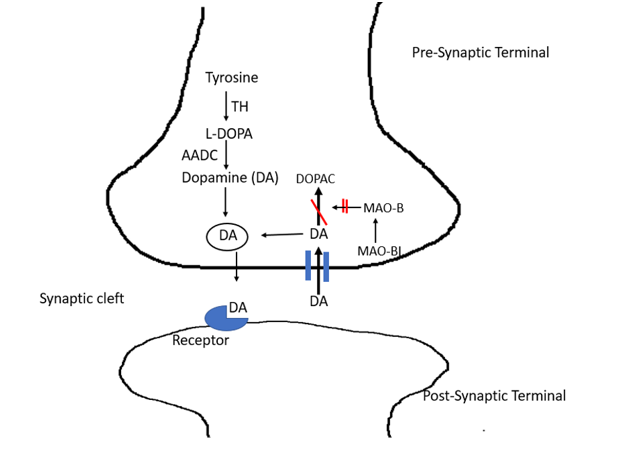
Figure- Inhibition of MAO-B enzymes by selegiline (TH- Tyrosine hydroxylase, AADC- Aromatic Amino acid Decarboxylase)
- It is an irreversible inhibitor of MAO enzymes. Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is a mitochondrial enzyme present in nerve and other tissues like gut and liver. It oxidatively deaminate and inactivate any excess neurotransmitters (including dopamine, nor-adrenaline, serotonin) that may leak out of synaptic vesicles.
- There are two classes of MAO enzymes: MAO-A and MAO-B. MAO-A acts upon nor-adrenaline, serotonin, adrenaline and tyramine whereas MAO-B acts upon dopamine, tyramine, benzylamine and N-methylhistamine. Parkinson’s disease is related to reduced amount of dopamine in specific parts of brain.
- In small doses, selegiline irreversibly inhibit the activity of MAO-B enzyme and reduce the breakdown of dopamine resulting in increased concentration and storage of dopamine in striatum. It also inhibits uptake of dopamine and nor adrenaline into presynaptic nerve. Thus, it helps to prolong the duration of improvement brought by levodopa.
- It can inhibit MAO-A if administered in higher doses (>10 mg). Inhibition of both MAO-A and MAO-B is required in treatment of MDD.
Pharmacokinetics of selegiline
- It is administered through oral route in form of capsule or oral disintegrating tablet (ODT). It is also available as transdermal patches. The oral route is mostly preferred in treating Parkinson’s disease as it provides low plasma concentration of drug. When used as transdermal patches, it helps to bypass ‘first pass metabolism’, hence transdermal patch is preferred in treatment of MDD as greater plasma concentration is achieved compared to oral route.
- Extensive metabolism takes place in liver by hepatic cytochrome P450 2A6, 2B6, and 3A4 with production of derivatives like methamphetamine mainly and L-amphetamine and desmethylselegiline in smaller quantity. Desmethylselegiline also possess MAO-B inhibiting activity. Amphetamine and methamphetamine may cause anxiety and insomnia. When taken with food, its bioavailability increases by 3-4 folds.
- Its half-life is long, around 39 hours. Dosage adjustment is required in patients with hepatic impairment.
Adverse Effects
- Some of its adverse effects are due to increase in central dopaminergic level. These effects include dyskinesia, nausea, hallucinations etc. Some other dangerous side effects include orthostatic hypotension, sudden sleep episodes, extrapyramidal symptoms, serotonin syndrome.
- It can also cause xerostomia and constipation. Transdermal patches may cause skin irritation at the site of application. When used in ODT form, it can cause irritation of buccal mucosa.
- The transdermal route of selegiline for MDD has black box warning for increasing risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in pediatric and young adult patients. Hence, it should be used with caution in such population.
Drug Interactions
- It may cause serious side effects when taken with other drugs like antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin- norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. Concurrent administration with SSRIs and pethidine may result in serotonergic reaction. It should be discontinued for some time before starting antidepressants.
- When its high dose is consumed with food, drink or supplements containing higher amount of tyramine (more than 150 mg) like yogurt, wine, cheese, ripe bananas etc. it can cause hypertensive crisis, raise in blood pressure to dangerous level.
- Centrally acting antimuscarinic drugs and amantadine may increase anti-parkinsonism activity of selegiline.
Contraindications
- Due to its risk of sudden elevation in blood pressure, it is not used within ten days of elective surgery.
- Transdermal patches of selegiline are not used in children younger than 12 years and in patients having pheochromocytoma.
- Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to selegiline.
- ODT form of selegiline is not recommended in patients with hepatic impairment. It is not used in patients with creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min.
- Contraindicated in patients with convulsive disorder.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526094/
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01037
- Heinonen Eh et al. A review of the pharmacology of selegiline. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1991; 136: 44-59.
- Magyar K. The pharmacology of selegiline. International Review of Neurobiology. 2011; 100: 65-84.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- Pharmacology and pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. 7th edition.
- A textbook of Clinical Pharmacology and therapeutics. 5th edition.