What is antimicrobial resistance?
- Antibiotics are becoming less effective in fight against microbial infections. Many decades after the discovery of first antibiotic in 1920s, bacterial infections have again become a threat. Resistance has been seen to almost all antibiotics developed.
- The reasons behind this are overuse and misuse of antibiotics, lack of new drug development by pharmaceutical industry and their wide use as growth supplement in livestock and for agricultural use. Incorrectly prescribed antibiotics also give rise to resistance and expose patients to potential complications of antibiotic therapy.
- WHO had published its first ever list of ‘antibiotic-resistant’ priority pathogens. Among them, Staphylococcus aureus is the major cause of morbidity and mortality, especially with emergence and spread of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MARS). Antibiotic-resistant gram-negative infections are also increasing at alarming rate.
- Thus, plant derived phytochemicals which can be alternative to antibiotics have been extensively studied over the past decade.
Cannabis- History
- Cannabis sativa, commonly known as ‘hemp’ is popular as a narcotic. However, it is a powerful medicinal plant that have been used in folk medicine for centuries.
- In past days, cannabis was used in treating rheumatoid arthritis, constipation, malaria, disorders of female reproductive system and other health problems.
- Cannabis gained some attention in medical science in middle of 19th century. However, it lost its medicinal value after removal from US Pharmacopoeia due to its potential to lead to insanity. Following this, it was termed illegal to use cannabis and it earned bad reputation.
- However, since recent years researchers are exploring its efficacy in treatment of epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, antiemetic effect, multiple sclerosis, analgesia and some other neurological disease. Many countries have legalized its cultivation and medicinal use.
- Few days before, the first over-the-counter (OTC) topical drug containing cannabidiol extract is approved by FDA. The product name is Elixicure which is non-addictive pain relief cream to be used in inflammation, swelling and pain.
Potential in Fight against Microbial Infection
- From a long time, cannabis has been regarded as possessing an antibacterial activity against some pathogenic bacteria. Cannabis contain cannabinoids which possess antibacterial properties. Five major cannabinoids present are cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and cannabinol (CBN).
- Wasim and co-workers had tested ethanol and petroleum extract of cannabis leaves which showed inhibitory effect on both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
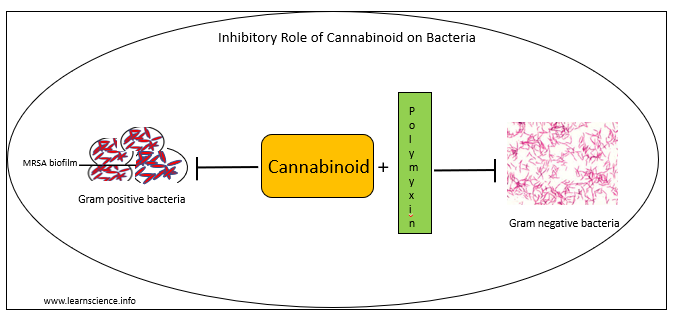
- A recent study had found that cannabinoids possess activity against MRSA. MRSA forms biofilms on necrotic tissues and medical devices which is an important virulence factor for its persistence in host body and the environment and its resistance. Cannabinoids is found to suppress biofilm formation. CBG could even eradicate pre-formed biofilms of MRSA.
- The formation of non-growing, dormant ‘persistent’ subpopulations of S. aureus which are highly tolerant to antibiotics is another major challenge of MRSA treatment. This is also cause of relapsing S. aureus infections like osteomyelitis and endocarditis. CBG is also effective against persister cells in dose dependent manner.
- Cannabinoids (particularly CBG) in combination with polymyxin B are also effective against gram negative bacteria like E. coli. In multi-drug resistant gram-negative pathogens, CBG act on the inner membrane.
- CBG is non-sedative and non-psychotropic.
- Cannabinoids show broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and thus, represents an attractive lead for new antibiotic drugs. Its potential to fight against antibiotic resistance may be revolutionary.
References
- Głodowska, Martyna. Cannabis sativa L. and its antimicrobial properties – A review (2016).
- Ventola CL. The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis Part 1: Causes and Threats. P T. 2015 Apr; 40(4): 277–283.
- Farha MA, EI-Halfawy OM, Gale RT, MacNair CR, Carfrae LA, Zhang X et al. Uncovering the Hidden Antibiotic Potential of Cannabis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020; 6(3): 338-346.
- Appendino G, Gibbons S, Giana A, Pagani A, Grassi G. Antibacterial Cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa: A Structure−Activity Study. J. Nat. Prod. 2008; 71(8): 1427-1430.