- Streptokinase is first thrombolytic agent introduced in medical field. It is a polypeptide derived from beta- hemolytic streptococci and have molecular weight of around 47000 D. It is potent activator of fibrinolytic enzyme system in human body.
- Thrombosis, blockage of blood vessels with clots can lead to acute myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke, both of which are leading cause of death. Blood clot can be dissolved by using thrombolytic agents like streptokinase.
- It is included in WHO Model List of Essential Medicines. Its use is rare nowadays due to introduction of new thrombolytic agents.
Indication of streptokinase
- It is FDA approved for treatment of acute ST segment acute myocardial infarction, arterial thrombosis or embolism.
- Used in treatment of deep vein thrombosis.
- Used in pulmonary embolism and arteriovenous cannula occlusion.
Mechanism of action of streptokinase
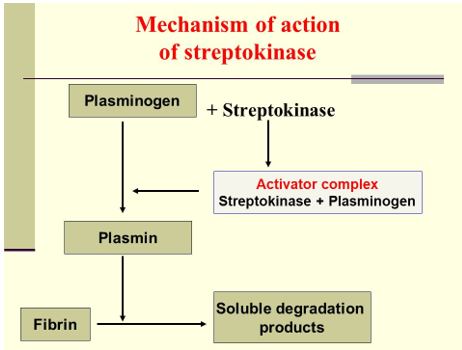
Figure – Mechanism of action of streptokinase (Source- slideplayer.com)
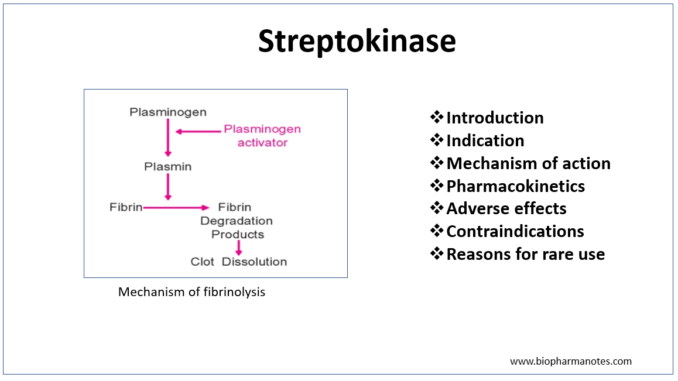
- Like other fibrinolytic agents, it also acts as plasminogen activator. Plasminogen is inactive proteolytic enzyme present in plasma which is converted to plasmin by plasminogen activator. The plasmin formed is needed to breakdown fibrin which is major component of blood thrombus. This results in dissolution of blood clot.
- Streptokinase forms a stable, non-covalent 1:1 complex with plasminogen leading to confirmational change. This change exposes active site in plasminogen leading to cleavage of Arg 560 on free plasminogen and results in formation of plasmin. The plasmin formed binds with fibrin and degrades fibrin clots, fibrinogen and other plasma proteins resulting in dissolution of blood clot.
Pharmacokinetics of streptokinase
- It is available as freeze dried powder in vials. Its dose may vary according to the use. Administration within 6 hours of onset of symptoms is found to be effective in reducing mortality.
- Its half-life is between 23-29 minutes. In some cases, its half life may increase up to 89 minutes.
Adverse effects
- Hemorrhage is major side effect. it cannot distinguish between fibrin of thrombus and fibrin of beneficial hemostatic plug. It is antigenic and can cause hypersensitivity reaction in around 2 % of patients.
- It can cause fever, hypotension and arrhythmia.
Contraindication
- Contraindicated in patient with active bleeding or hemorrhagic disorder, with serious GI bleeding within 3 months.
- Contraindicated in patients with history of hypertension.
- It is contraindicated in patients with intracranial neoplasm, recent stroke, intraspinal surgery or surgery within 2 months.
- It is pregnancy category C drug. Its effect on fetus in unknown and is used in pregnancy only in life threatening conditions.
- It is used with caution in patients with organ biopsies, previous puncture of a non-compressible vessel, infective endocarditis.
Reasons for its rare use
- It is less effective compared to newer more fibrin- specific tissue plasminogen activators like alteplase.
- It is antigenic and cause hypersensitivity reaction and other side effects.
- Once it is administered in patient, its second use in same patient may not be possible. It’s because streptokinase is antigenic, and antibodies may be produced in response to earlier dose which may cause neutralization of streptokinase.
- If the patient has history of streptococcal infection, antistreptococcal antibodies present in his body may inactivate certain fraction of initial dose of streptokinase. In such cases, loading dose is required.
References
- Brogden et al. Streptokinase: A Review of its Clinical Pharmacology, Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Uses. Evaluations on New Drugs. Drugs volume. 1973; 357–445.
- Kunamneni et al. Streptokinase – The drug of choice for thrombolytic therapy. Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis. 2007; 23(1):9-23.
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00086
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553215/
- Goodman and Gillman’s Manual of Pharmacology.
- Pharmacology and pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- A Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.