- Celecoxib is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAIDs) used to treat pain and inflammation. Most of the NSAIDs used including aspirin, ibuprofen and indomethacin are associated with GI and bleeding risks. COX-2 inhibitors (coxibs) are introduced to reduce pain and inflammation without associated GI and bleeding risks. Celecoxib is 1st COX-2 inhibitor introduced in market.
- It was introduced in medical field in 1999.
Indications of Celecoxib
- Used in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- In acute pain and dysmenorrhea.
- To reduce number of adenomatous colorectal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis.
Mechanism of action of Celecoxib
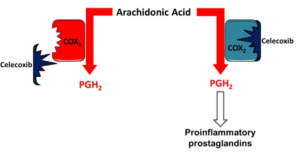
Figure 1- Selective inhibition of COX-2 by Celecoxib
- It selectively inhibits COX-2 (Cyclooxygenase 2) and prevent synthesis of prostaglandins which are important mediator of pain and inflammation in the body.
- COX-1 and COX-2 are responsible for synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid. Most of the NSAIDS inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2. Most of the GI related side effects are due to inhibition of COX-1.
- Celecoxib, however, has a sulfonamide side chain which binds to hydrophilic region near active binding site of only COX-2 and inhibit it. Hence, it helps to reduce pain and inflammation without any GI related side effects.
Pharmacokinetics of Celecoxib
- It is mostly administered through oral route. Peak plasma concentration is observed after 3 hours of oral administration. When administered with high fat meal, peak plasma levels were delayed for about 1- 2 hours. Co-administration with magnesium and aluminum containing antacid result in reduction in its plasma concentration.
- Its half-life is about 11 hours.
- It binds extensively to plasma protein (mainly albumin). It undergoes hepatic metabolism by cytochrome P450 2C9 and very little (around 3%) is excreted unchanged in urine and feces.
- Around 57% of drug is excreted through feces and 27% through urine.
Adverse effects
Some of the possible side effects include:
- Cardiovascular complications like stroke and heart attack.
- Dizziness.
- Abdominal bloating, diarrhea.
- Severe allergy or anaphylactic shock.
- Rashes, sore throat, flu like symptoms.
Contraindications
- It should be avoided in patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease.
- Contraindicated in patients allergic to sulfonamide and NSAIDs.
- In liver or kidney damage.
- In pregnancy and breastfeeding mothers.
- Contraindicated for pediatric use.
Drug Interactions
- It increases plasma lithium level. Coadministration of Diflucan increases its plasma level.
- Concurrent administration with warfarin may increase bleeding complications.
References
- Antoniou K, Malamas M, Drosos AA. Clinical pharmacology of celecoxib, a COX-2 selective inhibitor. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007; 8(11): 1719-32.
- Nissen et al. Cardiovascular Safety of Celecoxib, Naproxen, or Ibuprofen for Arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2016; :2519-2529.
- Clemett D, Goa KL. Celecoxib: a review of its use in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and acute pain. Drugs. 2000; 59(4): 957-80.
- https://www.pfizermedicalinformation.ca/en-ca/celebrex/action-and-clinical-pharmacology
- Current Therapy in Pain. 2009, Pages 59-72.