- 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) is thiol analogue of hypoxanthine. 6-MP and 6- thioguanine are first purine analogue to be used as antineoplastic agent.
- It is included in World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
Indication of 6- Mercaptopurine
- Used in treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, especially in children.
- Used to treat choriocarcinoma and chronic myelogenous leukemia.
- In treatment of steroid unresponsive inflammatory bowel disease.
Mechanism of action of 6- Mercaptopurine
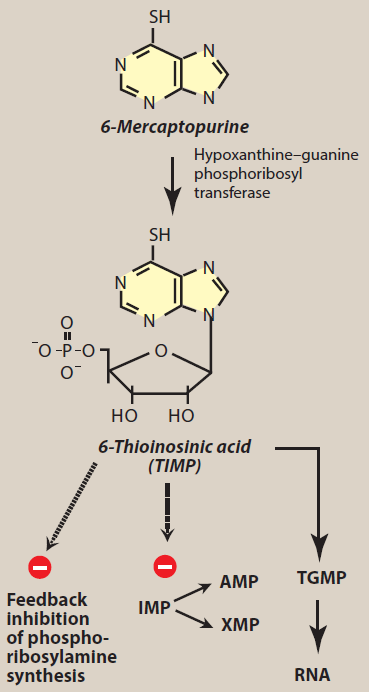
Figure- Mechanism of action of 6 mercaptopurine (IMP- Inosine Monophosphate, AMP- Adenosine Monophosphate, XMP- Xanthosine Monophosphate) (source- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews)
- After administration, it penetrates the target cells and get converted to nucleotide analogue- 6-MP ribose phosphate (6- thioinosinic acid or T-IMP). Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT) plays important role in addition of ribose phosphate group.
- 6-thioinosinic acid inhibit first step of denovo synthesis of purine ring. It inhibits conversion of inosine monophosphate to adenine and guanine nucleotides which are building blocks of RNA and DNA. It is converted to thio-guanine monophosphate which is phosphorylated to di and tri phosphates and incorporated into RNA. Hence, it results in non-functional RNA and DNA.
- It also causes feedback inhibition of denovo purine synthesis.
Resistance
Resistance may occur due to following reasons:
- Decreased level of HGPRT leading to decreased biotransformation of 6-MP to corresponding nucleotide.
- Increased dephosphorylation of drug.
- Increased metabolism of drug to thiouric acid or other metabolites.
Pharmacokinetics of 6- Mercaptopurine
- It is absorbed orally. The absorption is however incomplete. It is widely distributed throughout the body. CSF penetration is minimum. It is metabolized rapidly by xanthine oxidase. It along with its metabolites is excreted by kidneys.
- Its bioavailability can be hampered by first-pass metabolism in liver.
Adverse effects
- Its adverse effect is mainly related to bone marrow and GI tract. Bone marrow depression develops slowly and results in decreased number of WBCs, RBCs and platelets.
- It can cause nausea, vomiting, reversible jaundice and hyperuricemia. Allergic reactions are rare.
Drug Interactions
- Allopurinol which inhibits xanthine oxidase inhibit metabolism of 6-MP. Hence, its dose should be reduced when used in combination with allopurinol.
- It is known to interact with drugs like febuxostat, azathioprine and olsalazine.
Contraindications
- It is contraindicated in patient with anemia, low number of platelet and WBC count.
- Contraindicated in patients allergic to mercaptopurine.
- Contraindicated in renal patients and patient with abnormal liver function test.
- It is contraindicated in pregnancy.
References
- Bruce B, Gary E. American Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology. 1993; 80-86.
- https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-5903/mercaptopurine-oral/details/list-contraindications
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. 7th edition.