Introduction of Neuroleptanalgesia
- Neuroleptanalgesia is a method of IV anesthesia which combines the use of neuroleptic (antipsychotic) drug with opioid analgesics. It is a semiconscious non-reactive state. It is different from usual general anesthesia as patient is awake and cooperative during surgery.
- Neuroleptics used induce mental detachment and state of apathy (unresponsiveness). Opioid analgesics used produce relief from pain.
- The term neuroleptanalgesia was coined by the anesthesiologists De Castro and Mundeleer in 1959.
- In some surgical procedures like neurosurgical procedures, patient’s cooperation is required during surgery. In such conditions, techniques which produce effective analgesia without unconsciousness are desirable. General anesthetics are not suitable as they produce loss of consciousness. Thus, neuroleptanalgesia are used in such situations.
- Neuroleptanalgesia is characterized by following:
- Sleepiness without total unconsciousness
- Analgesia
- No voluntary movement
- Physiological indifference to the environment
- Satisfactory amnesia
- Suppression of autonomic reflexes
- Maintenance of cardiovascular stability
- Initially, around 1960s the combination used for this purpose was of phenoperidine and haloperidol which was subsequently replaced in 1980s by a combination of fentanyl (opioid analgesic) and droperidol (neuroleptic). These combination premixes are highly popular despite the fixed concentrations of the two drugs and the pharmacokinetic mismatch between the durations of the different agents.
- The technique has become less popular with the advent of more modern procedural sedation drug combinations. It is still rarely used today as a combination of 2.5 mg droperidol and 50 μg (micrograms) of fentanyl in a ratio of 50:1.
Droperidol (C22H22FN3O2)
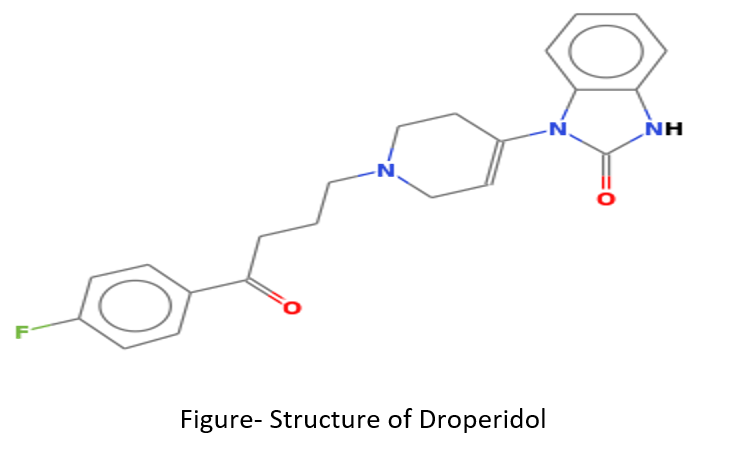
- It is a butyrophenone derivative and is very potent antipsychotic drug. Droperidol acts by binding to and blocking dopaminergic receptors (especially D2 receptors).
- It starts showing its actions within 5-10 minutes after IV administration which continue for around 6-12 hours.
- It also has anti-emetic and alpha-adrenergic blocking (adrenolytic) actions.
- Disadvantages of droperidol includes its long duration of action (in short surgical procedures like outpatient procedures), extrapyramidal actions like dystonia (abnormal muscle tone) and akathisia (a state of agitation, distress and restlessness), peripheral vasodilating effect and no pharmacological antagonist.
Fentanyl (C22H28N2O)
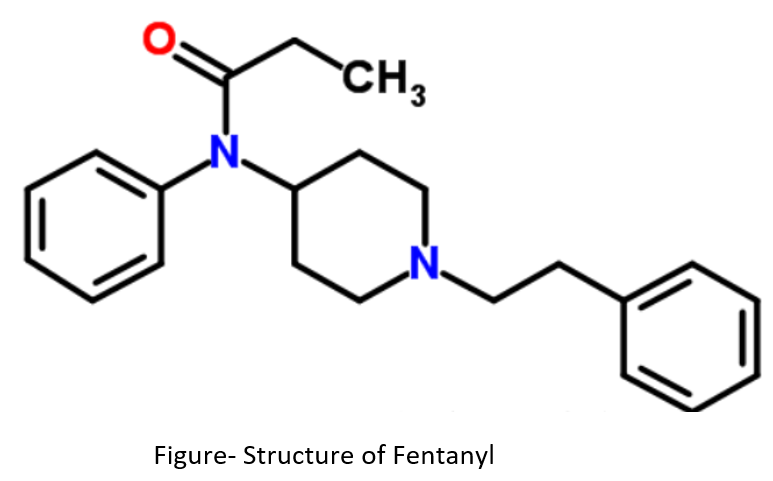
- It belongs to the group of 4-acylanilino piperidines and is a morphine-like opioid analgesic used as a supplementary analgesic in inducing general anesthesia. It is most potent opioid pain reliever available for use in medical treatment.
- Fentanyl binds to opioid receptors and increase dopamine level in central nervous system and thus produces state of relaxation, relieves pain and promotes a feeling of wellbeing (euphoria). It depresses respiratory center, cough reflex and constrict pupil.
- It acts rapidly after IV administration and lasts for about 30-60 minutes. As its duration of action is shorter compared to droperidol, supplementary doses of fentanyl (1 mcg/kg) may be needed after 20 minutes.
- Some disadvantages of using fentanyl are it produces emesis, respiratory depression, miosis and muscular rigidity when used in large doses.
Advantages of Neuroleptanalgesia
- Availability of patient’s co-operation during the operative procedures such as eye, oral and orthopedic surgery, angiocardiography, myelography and bronchoscopy.
- Smooth onset and rapid post-anesthetic recovery.
- Less danger of hypotension and other circulatory disturbances.
- Since the combination don’t disturb cardiovascular system, it is found to be useful in old people and in poor risk cases.
- Suppression of vomiting and coughing.
- Continued analgesia in postoperative period.
- The neuroleptanalgesia induced can also be continued with other general anesthetic agents like nitrous oxide-oxygen mixture and muscle relaxants.
Disadvantages of Neuroleptanalgesia
- Adverse effects may occur due to individual toxicity of drugs which includes hallucination, mental depression, extrapyramidal symptoms, respiratory depression. Controlled ventilation is necessary in case of respiratory depression.
References
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/308156
- https://dtb.bmj.com/content/4/7/25
- Small animal clinical pharmacology 2nd edition, 2008. Pages: 309-329.
- Sedation 6th edition, 2018. Page: 416-433.
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics 24th edition, 2015. Page: 119-121.