- Mycophenolate mofetil is 2-morpholinoethyl ester of mycophenolic acid (MPA). It is prodrug and is also known as cellcept or MMF.
- Mycophenolic acid is antibiotic obtained from various Penicillium fungal species and was used to treat autoimmune diseases in early 1970s. Due to its severe gastrointestinal effects, its use was discontinued and its new semi-synthetic ester, mycophenolate mofetil was synthesized. Mycophenolate mofetil shows reduced gastrointestinal effect, higher efficacy and increased bioavailability when compared to MPA.
- Mycophenolate mofetil was marketed by Roche Pharmaceuticals and it was approved for medical use in 1995.
Indications of mycophenolate mofetil
- Used with cyclosporine and corticosteroids in prophylaxis of transplant rejection in renal, hepatic, or cardiac transplant.
- Its non-FDA approved uses include:
- Treatment of lupus associated nephritis and dermatitis in children.
- For treating autoimmune hepatitis which doesn’t respond to first-line therapy.
Mechanism of action of mycophenolate mofetil
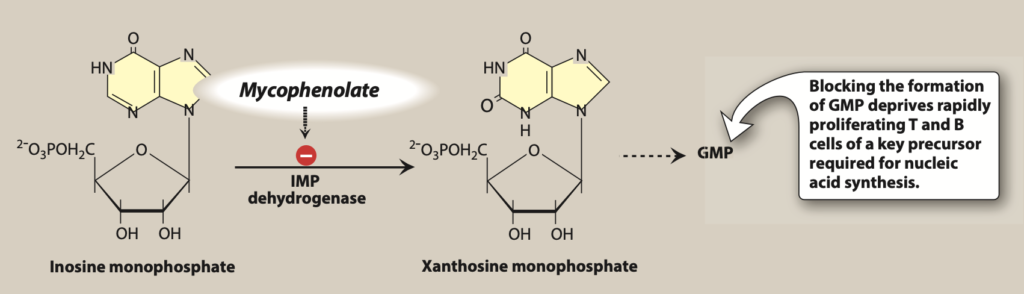
Figure- Mechanism of action of mycophenolate mofetil (Source- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6thedition)
- It is inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) inhibitor. As it is prodrug, it is rapidly hydrolyzed to its active form, mycophenolic acid after administration. Mycophenolic acid is selective, reversible, and non-competitive inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase.
- IMPDH convert inosine monophosphate (IMP) to xanthine monophosphate (XMP) and is rate limiting enzyme and play important role in de novo pathway of guanine nucleotide synthesis which is the major pathway involved in cell proliferation of B and T lymphocytes. Lymphocytes solely depend on de novo formation of purine production as they don’t use salvage pathway for purine synthesis unlike other cell types. Hence, the result is selective inhibition of proliferation of lymphocytes and their functions including antibody formation, cell adhesion and migration.
- It prevents adhesion of monocyte and lymphocyte to endothelial cells of blood vessels by inducing glycosylation of cell adhesion molecules.
Pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil
- It is administered via oral or IV route and is rapidly hydrolyzed to MPA after administration. It is rapidly absorbed in small intestine. Peak plasma concentration of MPA is achieved 60-90 minutes after oral administration. Food can delay the rate of absorption of MMF.
- Around 97% of MPA binds to plasma protein, albumin and is metabolized in liver. The major metabolite formed is MPAG (phenolic glucuronide of MPA) which is inactive. Major portion of drug is excreted as MPAG via urine. Very less amount (less than 1%) is excreted as MPA in urine.
- Its half-life is around 16 hours. Plasma concentration of MPA and MPAG may increase in patient with renal impairment.
Adverse effects of MMF
- Its major adverse effects are GI related effects including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. It can also cause urinary disturbances, headache, hypertension, and neutropenia.
- When used in high doses, it can increase risk of CMV (cytomegalovirus) infection. It can cause bone marrow suppression, especially anemia and leukopenia.
Drug Interactions of MMF
- Concurrent administration of antacids containing aluminum or magnesium may decrease absorption of mycophenolate mofetil. Hence, they should not be administered together. Tacrolimus may delay excretion of mycophenolate mofetil by impairing conversion of MPA to MPAG.
- Drug which affects enterohepatic circulation like cholestyramine may bind to free MPA in intestine and decrease its plasma concentration. Such combination should be avoided.
Contraindications
- Contraindicated in patient hypersensitive to MMF or any component of drug product.
- Its IV form is contraindicated in patient hypersensitive to Polysorbate 80 (Tween).
References
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00688
- https://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/2/1/184
- https://www.rxlist.com/cellcept-drug.htm#clinpharm
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Mycophenolate-mofetil
- Fulton B et al. Mycophenolate mofetil. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacy in renal transplantation. Drugs. 1996 Feb; 51(2): 278-98.
- Allison Ac et al. Mycophenolate mofetil and its mechanisms of action. Immunopharmacology. 2000 May;47(2-3):85-118.
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics