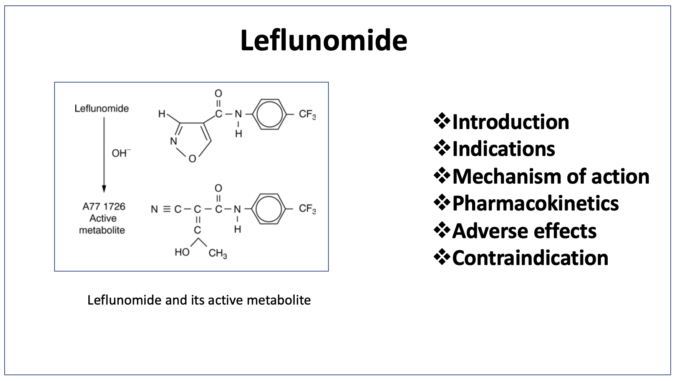
- Leflunomide belongs to class of drug called DMARDs (Disease Modifying Anti- Rheumatic Drugs). It is non-biological novel isoxazole derivative. Leflunomide got its FDA approval for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in 1999. Leflunomide is available as brand ARAVA.
- DMARDs are class of drugs used in treatment of RA. They can be used as monotherapy or in combination therapy. Some other DMARDs beside leflunomide include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, or sulfasalazine etc.
Indications of leflunomide
- FDA approved for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. It helps in improving physical function in RA patients and slows progression of structural damage. It can be used as monotherapy or in combination with other agents like methotrexate.
- In psoriatic arthritis.
Mechanism of action of leflunomide
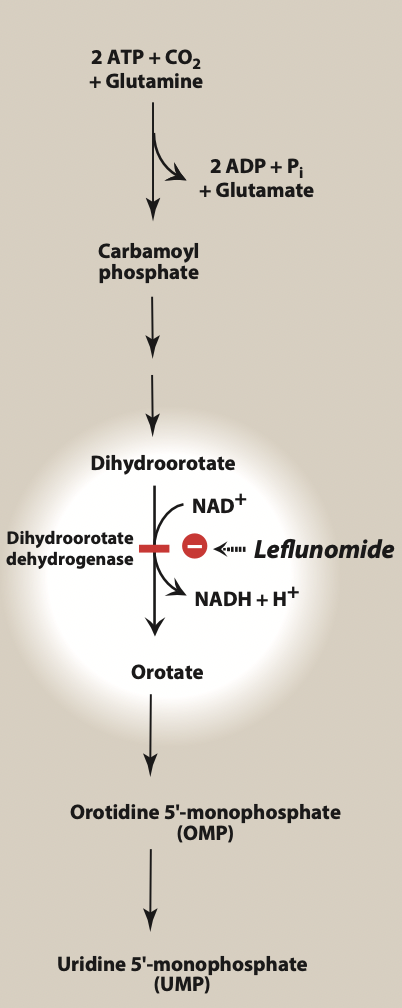
Figure- Site of action of leflunomide (Source- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews)
- It is pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor. It is a prodrug and gets converted to active metabolite, teriflunomide. Teriflunomide inhibit mitochondrial enzyme- dihydro orotate dehydrogenase (DHOHD). DHOHD is located in inner mitochondrial membrane and catalyze ubiquinone mediated oxidation of dihydroorotate to orotate in denovo synthesis of pyrimidine ribonucleotide uridine monophosphate (rUMP). Pyrimidine and purine are building blocks of DNA. Inhibition of DHOHD by teriflunomide lead to decrease in rUMP level.
- It also activates P53 which inhibits progression of G1 to S phase in cell cycle. This inhibits proliferation of activated and autoimmune lymphocytes which results in immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects.
Pharmacokinetics of leflunomide
- It is available as oral tablets and is well absorbed after oral administration. Its peak plasma concentration is achieved 6-12 hours after its administration. Due to the long half-life of active metabolite, leflunomide administration is initiated with loading dose of 100 mg once daily for 3 days and continued with maintenance dose of 20 mg/ day.
- Binding to plasma protein is high (around 99%). It is metabolized in gut wall, plasma and liver to its active form which than undergoes excretion by renal excretion as well as direct biliary excretion.
Adverse effects
- Some of its common adverse effects include rashes, diarrhea, elevation of hepatic enzymes, nausea, alopecia, abdominal and back pain.
- Serious and less common adverse effects include pancytopenia, interstitial liver disease, pneumonitis etc.
Contraindications
- It has teratogenic effects, so it is contraindicated in pregnancy.
- Contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment due to its hepatotoxic effect. Patients receiving leflunomide should be continuously monitored for level of serum hepatic enzymes.
- Contraindicated in patients with interstitial lung disease.
- It is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to leflunomide.
- Also contraindicated in patients with immunosuppression and impaired bone marrow function.
- Patients on leflunomide therapy should also be monitored for any sign of infection and complete blood counts.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10651393/
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01097
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557799/?report=printable
- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.