- Indapamide is lipid-soluble thiazide-like diuretics. Indapamide is an indole derivative of chlorsulphonamide and is chemically related to chlorthalidone. The presence of 2- methyl indoline ring makes it different from thiazide diuretics and is responsible for its lipophilicity.
- It was approved for medical use in 1977. It is also included in World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines and is also available as generic medicine.
Available Brand
Lozol
Indications of Indapamide
- Used as monotherapy or in combination with other anti-hypertensive agents to treat hypertension.
- To treat fluid and salt retention associated with CHF (Congestive Heart failure).
Mechanism of action of Indapamide
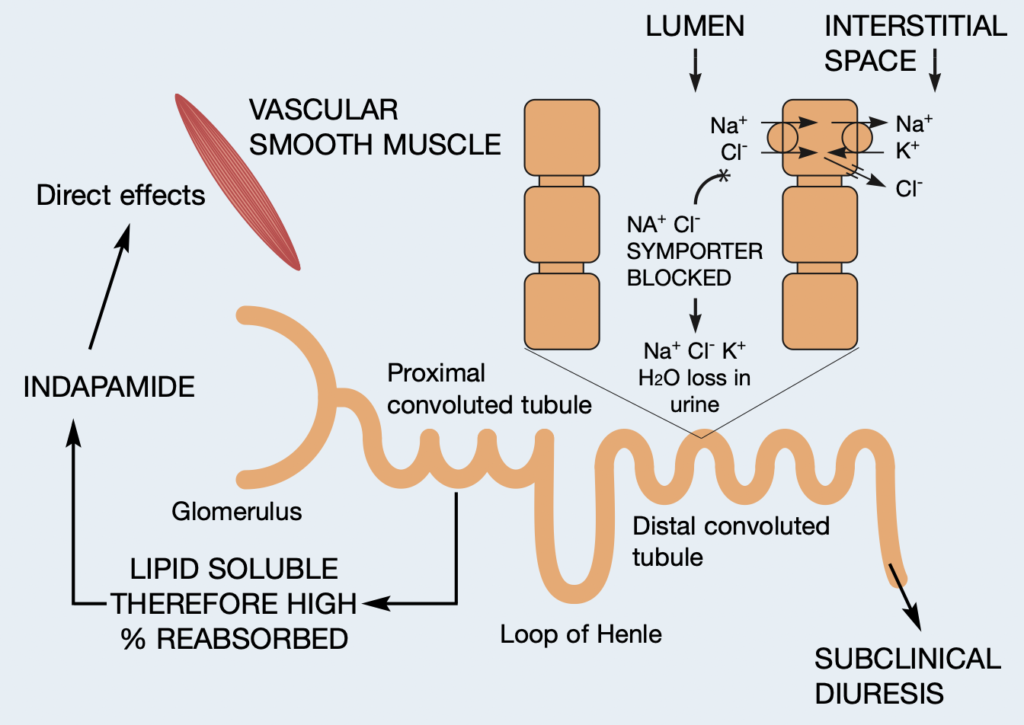
Figure- Pharmacological action of Indapamide (source- Livingstone K et al, 2008)
- It acts on proximal segment of distal convoluted tubule (DCT) of nephron and inhibits Na+/Cl– co-transporter. This results in decreased sodium reabsorption which leads to retention of sodium and water in nephron. The overall result is reduced plasma volume, reduced venous return, lower cardiac output, and decreased blood pressure.
Pharmacokinetics of Indapamide
- After oral administration, it is rapidly absorbed from the GI tract. Peak plasma concentration is observed 2-3 hours after administration. It can be administered with or without food. It is also available as sustained release form.
- Indapamide has long duration of action with plasma half-life of around 18 hours. When used in low dose, it is useful for treatment of mild to moderate hypertension. In larger doses, it causes diuresis. Due to long half-life, once daily dosing of indapamide is effective.
- Around 76-79% of administered drug is bound to protein. major protein to which it binds is alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. It is extensively metabolized in liver. 60-70% is excreted via urine and 16-23% via feces.
How to take Indapamide?
Iis available as oral tablet and is usually taken once a day in the morning. As it increases urination, it is better to not take this medicine during bedtime.
What to do if a dose is missed?
- If you miss the dose, take the missed dose as soon as you remember about it. But if it already is time for next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule.
- Avoid taking two doses at a time to make up for the missed dose.
Adverse effects
- It may cause side effects like nausea, vomiting, GI disorders, weakness, dehydration, and hypokalemia. Some other side effects include hypotension, irritability, agitation, increased blood glucose level, increased uric acid concentration, nervousness, rashes, and photosensitivity.
- Due to its hypokalemic effect, patients on indapamide therapy are advised to take potassium-rich food.
Drug and food Interactions
- When co-administered with digoxin, it increases the risk of digoxin toxicity. Indapamide and amiodarone when used together, can cause cardiac arrhythmia. It decreases excretion of lithium by kidney. Hence, when used with lithium, it can cause lithium toxicity.
- Alcohol may increase its effect of causing orthostatic hypotension. So, alcohol should be avoided by patients on indapamide therapy.
Contraindication
- Contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to sulfonamide.
- Contraindicated in severe hepatic and renal patients.
- Due to hypokalemic effect, it should not be used in patients with low potassium level.
- There are no adequate studies about its safety in pregnant and breastfeeding women.
- When used in diabetic patients, blood sugar should be continuously monitored as it can increase blood sugar level.
References
- Sassarda J etal. An overview of the pharmacology andclinical efficacy of indapamide sustained release. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology. 2005; 637–645.
- Chaffman M et al. Indapamide. A review of its pharmacodynamic properties and therapeutic efficacy in hypertension. Drugs. 1984 Sep;28(3):189-235.
- Livingstone K et al. Indapamide. Pract Diab Int September. 2008; 25 (7): 290-291.
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00808
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology. 6th edition.
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.