- Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system are two divisions of ANS (autonomic nervous system). Nervous system can be divided into CNS (Central nervous system) and PNS (Peripheral Nervous System). CNS consists of brain and spinal cord and PNS consists of somatic nervous system and ANS. Somatic nervous system controls movement of skeletal muscle and Autonomic nervous system controls automatic, involuntary physiological process like blood pressure, heart rate, digestion, respiration etc.
- Parasympathetic NS is associated with ‘rest and digest” response and sympathetic NS is associated with ‘fight or flight’ response of the body.
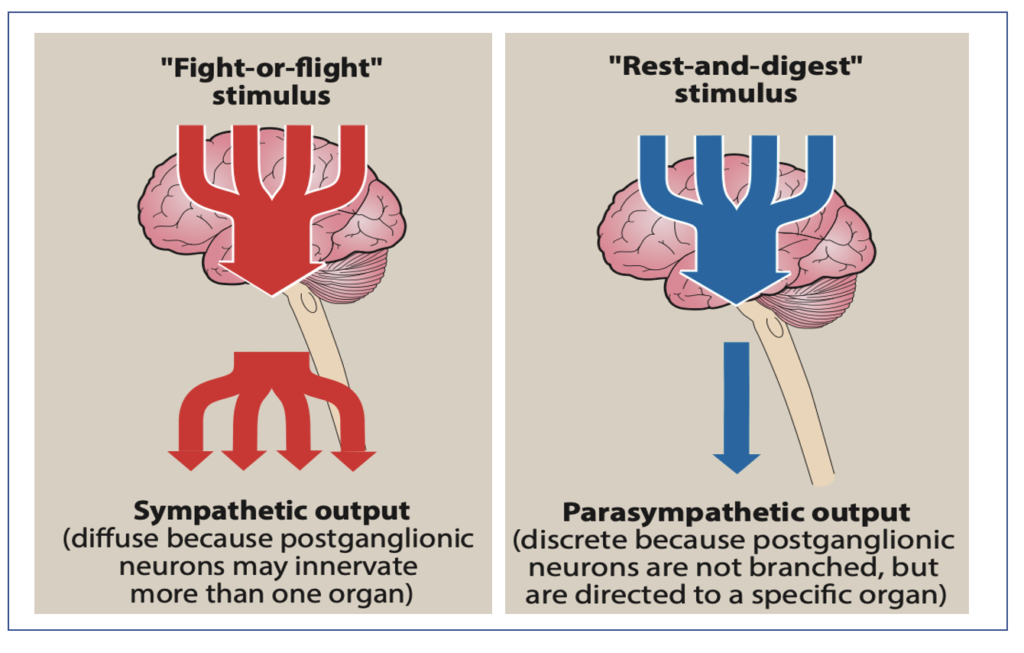
Figure source- Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
Difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
| Comparison | Parasympathetic | Sympathetic |
| Origin | Preganglionic fiber of parasympathetic NS arises from sacral region (S2 to S4) of spinal cord and from cranial nerves III (oculomotor), VII (facial), IX (glossopharyngeal) and X (vagus). | Preganglionic fiber arises from thoracic and lumbar region (T1 to L2). |
| Function | Helps to maintain homeostasis. Helps in essential body function like digestion and elimination of waste. | Helps in controlling body’s response during stressful situations like fear, trauma, cold, exercise etc. |
| Predominates | Predominates in ‘rest and digest’ situation. | In ‘fight or flight’ response of body. |
| Distribution | More limited distribution. | Widely distributed and innervates almost all effector systems in the body. |
| Postganglionic neurons | Not branched and directed to a specific organ. | Branched and innervate more than one organ. |
| Synapse | Preganglionic neurons are long, postganglionic neurons are short and ganglia are close to within the organs they innervate. | Preganglionic neurons are short compared to postganglionic neurons and axons of postganglionic neurons extend from ganglia to organs they innervate. |
| Action on heart rate (CVS) | Decreases heart rate. | Increases heart rate. |
| Effect on lungs | Constriction of bronchial tubes. | Dilation of bronchial tubes. |
| Effect on muscles | Relaxation of muscles. | Contraction of muscles. |
| Effect on pupil | Constriction | Dilation |
| Salivary gland | Increase in salivary secretion. | Decrease in salivary secretion. |
| Urinary output | Increase in urinary output. | Decrease in urinary output. |
| GI system | Increase in stomach movement and secretions. | Decrease in stomach movement and secretions. |
| Nerves | Cholinergic | Adrenergic |
| Outflow | Forms craniosacral outflow. | Forms thoracolumbar outflow. |
Similarities
- They both are part of peripheral nervous system and hence autonomic nervous system.
- Both control involuntary functions of body.
References
- https://imotions.com/blog/nervous-system/
- https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-sympathetic-and-vs-parasympathetic-nervous-system/
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. 7th edition.