- Varenicline is the first approved nicotinic receptor partial agonist to treat smoking addiction. It is a prescription medicine and is not available OTC.
- It was introduced in market by Pfizer. FDA approved its generic version developed by Par Pharmaceutical on August 11, 2021. It is included in World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
Indications of varenicline
- It is the first drug of choice for smoking cessation as it is effective in preventing both short- term and long-term relapse of smoking. Some other medications used to stop smoking are bupropion, nicotine replacement medications (gum, patch, lozenge, nasal spray, and inhaler). Varenicline is equally efficacious to nicotine replacement therapy and has superior effect than bupropion in smoking cessation.
- Varenicline is also used for symptomatic treatment of dry eye disease.
Mechanism of action of varenicline
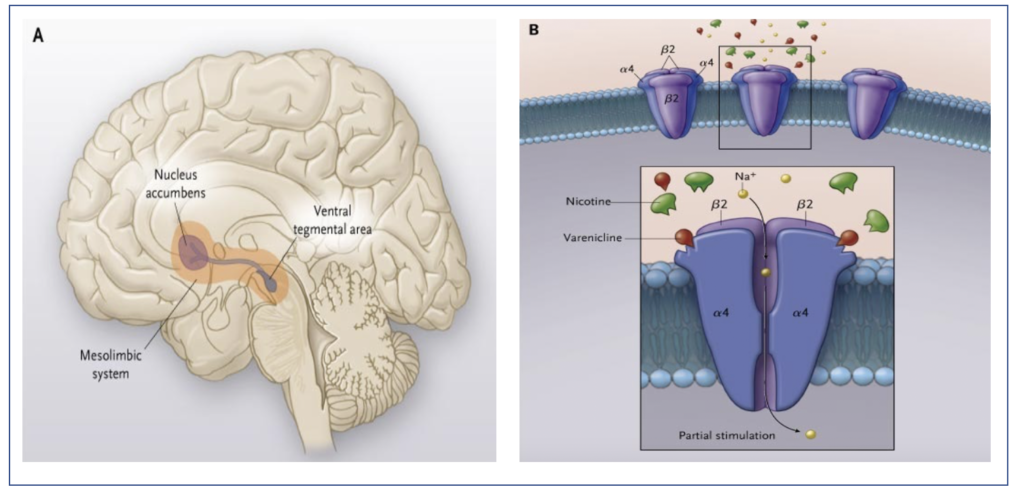
- It is an alpha-4 beta-2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist. Nicotine is the main constituent of tobacco which is responsible for smoking addiction. Nicotine stimulates central nicotinic acetylcholine receptors causing release of various neurotransmitters like dopamine. Binding of dopamine to dopaminergic receptors in ventral tegmental area and dopamine release in the shell of nucleus accumbens are important in drug inducing reward.
- Varenicline blocks the effect of nicotine on brain by competitively inhibiting the binding of nicotine with alpha-4 beta-2 receptor. It results in inhibition of dopaminergic activation leading to decrease in craving and withdrawal symptoms that occurs when a person try to stop smoking.
Pharmacokinetics
- Varenicline is orally administered and comes in form of tablet. Therapy is started before one or two week of quitting smoking. It is usually taken after food to prevent gastric upset. The duration of treatment may be 6 months or longer.
- Its elimination half-life is around 24 hours. Its metabolism is limited. Around 90% of the drug is excreted unchanged in urine.
Adverse effects
- Some of the common adverse effects associated with varenicline intake are sleep disturbance, insomnia, headaches, drowsiness, agitation, constipation, and abnormal vivid dreams.
- Varenicline may also cause erythema multiforme, photosensitivity and Steven- Johnson syndrome. It may increase the risk of pancreatitis.
Contraindications/ Warnings
- As varenicline can cause serious skin reactions, patients with erythema multiforme or Steven- Johnson syndrome should not take it. It should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment, seizure, and psychiatric disorder.
- FDA has issued warning to stop the medication if there is any mood or behavior related side effects.
- Contraindicated in pregnancy.
References
- Bonowitz NL et al. Pharmacology of Nicotine: Addiction, Smoking-Induced Disease, and Therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2009; 49: 57–71.
- Burke MV etal. Varenicline for smoking cessation: a narrative review of efficacy, adverse effects, use in at-risk populations, and adherence. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016; 10: 435–441.
- Hays et al. Varenicline for Tobacco Dependence. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359: 2018-2024.
- A textbook of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th edition.
- https://www.formularywatch.com/view/fda-approves-generic-of-chantix-pfizer-s-smoking-cessation-drug
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534846/
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01273
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Varenicline