- Protein synthesis (translation) in eukaryotes begins after methionyl charged initiator t-RNA is delivered to ribosomes by eIF2 (eukaryotic initiation factor 2). eIF2 is one among many important eukaryotic initiation factors.
- There are many different eukaryotic initiation factors which play important role in translation initiation including eIF4B, eIF4F, eIF5, eIF6.
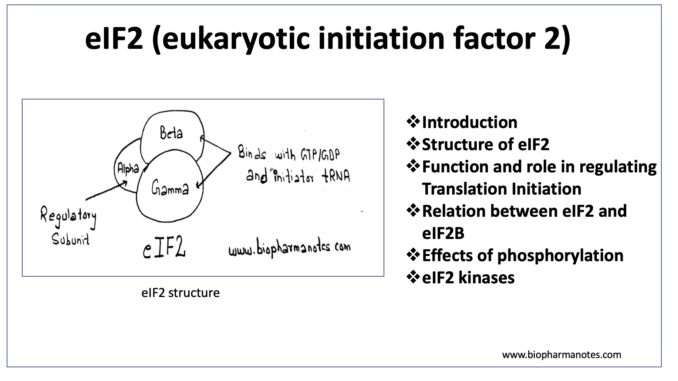
Structure of eIF2 (eukaryotic initiation factor 2)
- It is heterotrimer and consist of three dissimilar subunits, alpha (a), beta (b) and gamma (g) subunits.
Alpha subunit– is the regulatory subunit and is the main target for phosphorylation in serine 51 residue.
Beta and gamma subunit– These two subunits have binding site for GTP or GDP, initiator t-RNA and the P site of the 40S ribosomal subunit.
Function and role in regulating translation initiation

Figure 2- Role of eIF2 in translation initiation (Source- The International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 1999)
- It delivers methionyl charged initiator t-RNA (MET) to 40S ribosomal subunits and make the 43S preinitiation complex. It binds with GTP and methionine charged tRNA and forms ternary complex (eIF2/GTP/ Met-tRNA). And it also helps to ensure that start codons are correctly recognized.
- Without it, initiator MET cannot be delivered to P site on the 40S subunit and without initiator methionine group, translation cannot be started. It controls the global rate of protein synthesis. By regulating its activity, one can control the amount of protein synthesis.
Relation between eIF2 and eIF2B
- It is active when it binds to GTP. Binding with GTP increase its affinity for Met-tRNA. After completion of initiation, eIF5 triggers GTP hydrolysis and eIF2-GDP leaves ribosome together with eIF5. eIF2- GDP complex has less affinity for Met- tRNA.
- To engage in further rounds of binding with and delivering Met-tRNA for initiation of protein synthesis, it needs to bind with GTP. For this eIF2B play an important role. eIF2B is initiator protein having pentamer structure. It acts as enzyme, first removes eIF5 and it exchanges GDP for GTP on eIF2 and recycles eIF2- GTP for another round of initiation.

Figure 2- eIF2- eIF2B cycle
Effect of phosphorylation of eIF2
- Phosphorylation of a subunit of eIF2 have effect on GEF activity of eIF2B. eIF2B has more affinity for the phosphorylated eIF2(aP) than for the unphosphorylated one. We can say that phosphorylation of its alpha subunit on a subunit convert it from substrate of eIF2B into competitive inhibitor.
- The phosphorylated eIF2 uses all the available eIF2B and inhibit the eIF2B’s guanine nucleotide exchange reaction on eIF2- GDP complex. Hence, this prevents formation of eIF2.GTP-Met-tRNA complex (ternary complex) and inhibits global protein synthesis.
- Among various phosphorylation sites in eIF2a, serine 51 is the important one for translational control. Phosphorylation may occur during various conditions or disease conditions. Various stimuli that can activate its phosphorylation include:
- Viral infection
- Nutrient deprivation
- Heme-deprivation
- Alcohol, heavy metal ions
- High temperature
- Hypoxia or ischemia
- Various disease condition which involves its phosphorylation are:
- Epilepsy
- Brain ischemia
- Diabetes
- Various forms of viral infection like polio.
eIF2 Kinase
- Protein kinases are enzymes which transfer phosphate group from high energy compound like ATP on other proteins. eIF2 kinases phosphorylate alpha subunit of eIF2. They belong to Ser/ Thr family of protein kinases and require phosphorylation to be active. They also require binding to some other molecule in addition to phosphorylation. The binding with another molecule can turn them active or inactive.
- Four major eIF2 kinases include HRI, PKR, GCN2 and PERK.
HRI/ EIF2AK1 (Heme Regulated Inhibitor of Protein synthesis)
- It is activated when heme is not bound to its kinase insert domains due to heme deficiency and remains inhibited when bound to heme. It is usually activated during heavy metal poisoning.
PKR/EIF2AK2 (Protein Kinase R/ double stranded RNA activated eIF2a protein kinase)
- It is activated during viral infection due to binding of ds viral DNA to its two conserved ds DNA binding domain. During viral infection, PKR gets activated, phosphorylate eIF2a which leads to inhibition of protein synthesis and prevent the virus from taking over the ribosomes.
PERK/ EIF2AK3 (PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum eIF2a kinase)
- It is present in ER membrane and is activated during ER stress due to release of binding immunoglobulin proteins (GRP78) from its ER luminal domains. It remains inactive when bound to this protein.
GCN2/ EIF2AK4 (General controlled Nonderepressible 2)
- It is activated by binding of uncharged histidyl tRNA to its regulatory domains during nutrient/ amino acid deprivation.
References
- Adomavicius T et al. The structural basis of translational control by eIF2 phosphorylation. Nature Communications. 2019; 10: 2136.
- Kimball SR et al. Eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999 Jan; 31(1): 25-9.
- Taniuchi S et al. Integrated stress response of vertebrates is regulated by four eIF2α kinases. Scientific Reports. 2016; 6: 32886.
- Donnelly N et al. The eIF2α kinases: their structures and functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Oct; 70(19): 3493-511.
- The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. Volume 31, Issue 1, January 1999, Pages 25-29.