- Statins or HMG CoA reductase inhibitors are lipid lowering agents and are among the most widely used drugs in cardiovascular pharmacology.
- Some commonly used statins are
- Atorvastatin
- Fluvastatin
- Rosuvastatin
- Pravastatin
- Simvastatin
- Lovastatin
- Simvastatin is included in World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
Indications of statins
- Effective in lowering plasma cholesterol in all type of hyperlipidemias. In patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, due to lack of LDL receptors, they are less efficacious.
- Used for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
- They are used in patients with high risk factors like in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, myocardial infarction, patients with LDL cholesterol level˃ 190%.
Mechanism of action
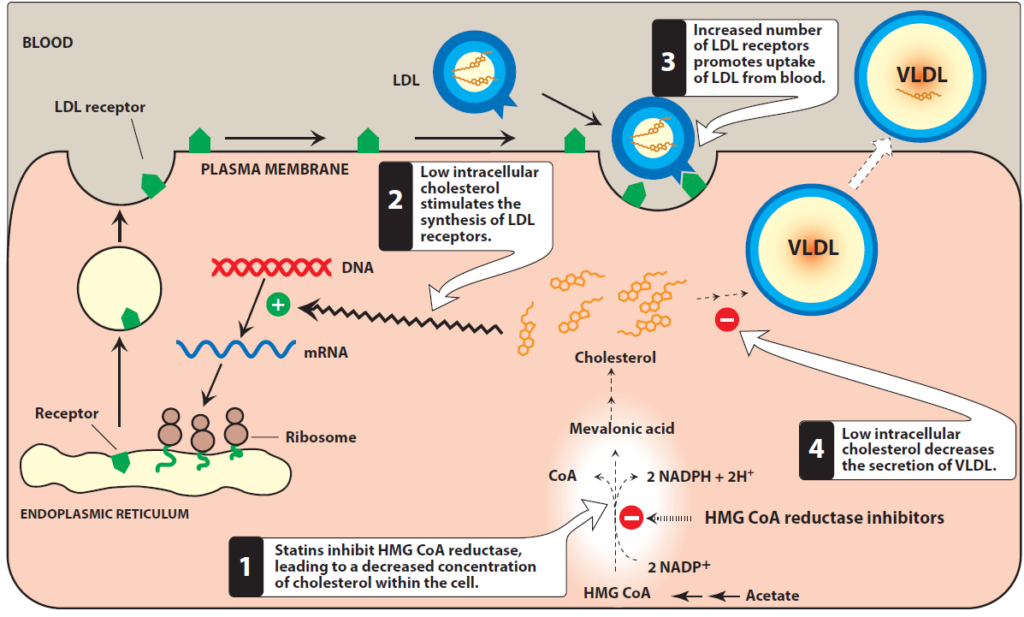
Figure 1- Inhibition of cholesterol synthesis by statins (Source- Lippincott’s Illustration of Pharmacology)
- Statins are structural analogues of HMG CoA (Hydroxy Methyl Glutrayl Coenzyme A) and are competitive inhibitor of HMG CoA reductase enzyme. HMG CoA reductase enzyme catalyze an early, rate-limiting step; conversion of HMG CoA to mevalonate, in cholesterol biosynthesis. Hence, statins inhibit denovo synthesis of cholesterol and reduce internal supply of cholesterol.
- Statins inhibit this rate limiting step everywhere, but most important site is in the liver. As the free cholesterol content within hepatocytes is reduced, synthesis of LDL receptor increases to bind and internalize circulating LDLs to extract cholesterol from them. The decrease in cholesterol synthesis and increase in catabolism of LDL leads finally in decreased plasma cholesterol level.
- They also decrease triglyceride level and may increase HDL cholesterol level. More potent statins like atorvastatin, rosuvastatin and Fluvastatin also have significant effect on VLDL. Their effect on VLDL is due to increased VLDL clearance.
Pharmacokinetics of statins
- Simvastatin and lovastatin are used as pro-drugs (inactive lactones) and all other statins are administered in their active form. They are administered though oral route and intestinal absorption varies between 30-85% according to statins.
- They are metabolized in liver. The metabolites of all statins have some HMG CoA reductase activity except fluvastatin and pravastatin. Excretion takes place mainly though Biles and feces and small extent of urinary excretion.
- Statins with short half-life are mostly taken in evening as the production of endogenous cholesterol is high at night.
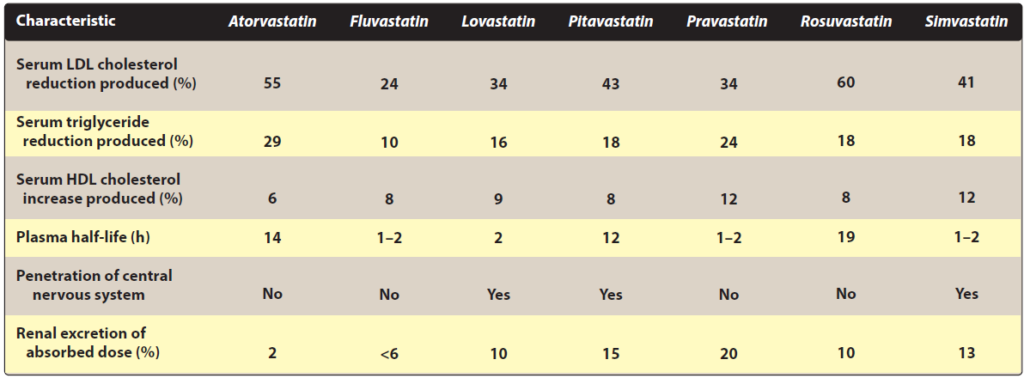
Figure- Different Pharmacokinetic parameter of statins (Source- Lippincott’s Illustration of Pharmacology)
Adverse Effects
- They are well tolerated drugs. Adverse effects are mild and dose dependent.
- The most common serious adverse effect is myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. They may cause reversible rise in hepatic aminotransferase level and plasma creatine kinase level. Some other rare side effects include gynecomastia, impotence, memory loss, insomnia, mood changes and depression.
- There is rare chance of increase in diabetes and cataract.
Drug Interactions
- When used in combination with fibric acid derivatives and nicotinic acid derivatives, plasma CPK level may increase.
- They may potentiate the effect of warfarin. So, patients receiving combination therapy should undergo regular monitoring of international normalized ratio (INR). Plasma concentration of some statins are increased by grapefruit juice.
- Their toxic effect increases when it is taken with drugs which inhibit CYP enzymes including HIV protease inhibitors, macrolides, antifungals and antiarrhythmic drugs.
Contraindications
- Contraindicated in pregnancy, in woman planning to be pregnant and in breastfeeding women.
- Contraindicated in patients with liver disease.
- They are contraindicated in children.
References
- Sirtori CR. The pharmacology of statins. Pharmacol Res. 2014; 88: 3-11.
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 24th edition.
- Goodman and Gillman Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
- Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Pharmacology, 6th edition.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430940/